Springs Servlets
Spring MVC
📘 Servlet
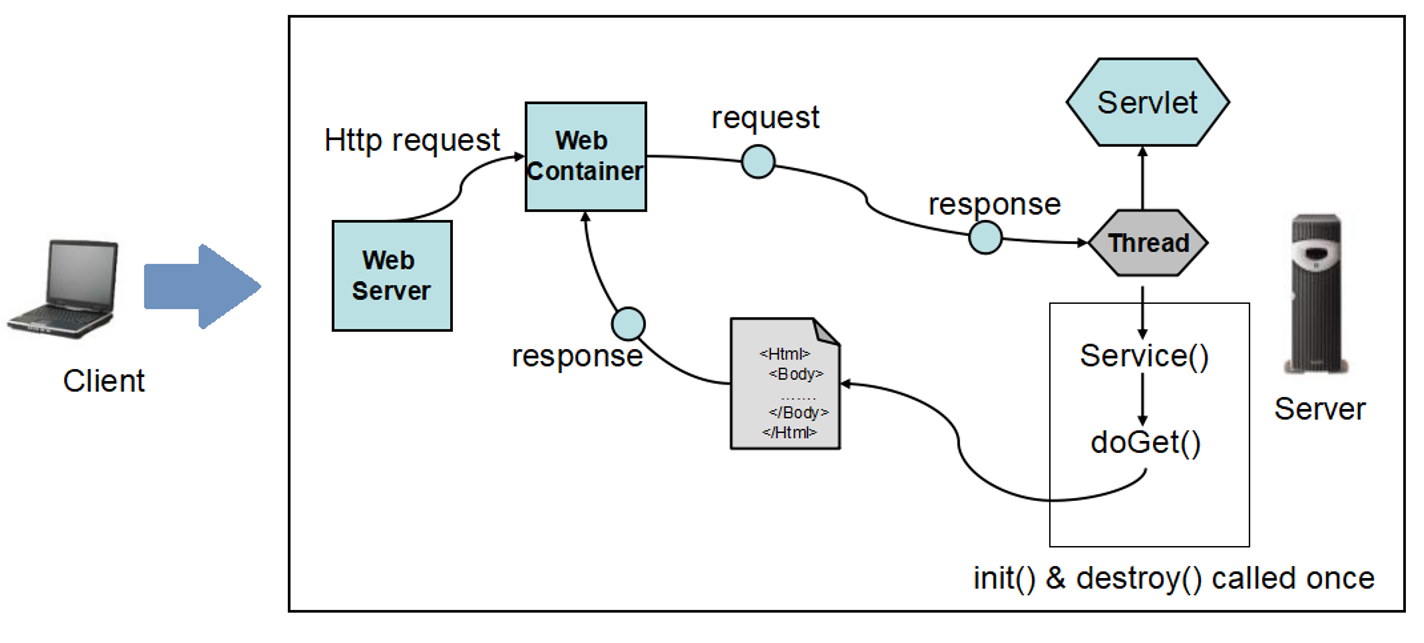
A servlet in Java is a server-side technology that enables the handling of requests and responses between a client and a server.
Servlets are Java classes that extend the functionality of web servers and allow developers to dynamically generate web pages and other resources based on user requests.
1 Overview: JSP, Servlets and DAOs
JSP (JavaServer Pages) and servlets are server-side Java technologies that work together to build dynamic web applications.
JSPs provide a way to generate HTML pages dynamically using Java code, while servlets handle incoming HTTP requests and provide responses back to the client.
JSP, servlets, and DAOs are technologies that have been around for many years and are still in use today.
When combined with a DAO (Data Access Object) layer, JSPs and servlets can interact with a SQL database to store and retrieve data.
The DAO layer acts as an intermediary between the application and the database, handling the low-level details of data access and providing a consistent interface for the rest of the application to use.
JSP and servlets were introduced in the late 1990s as part of the Java EE (Enterprise Edition) specification, which aimed to provide a platform for building scalable and robust enterprise applications. These technologies are still commonly used today.
Using this combination of JSPs, servlets, and DAOs, developers can build powerful, scalable, and maintainable web applications that can handle complex data and business logic.
The use of DAOs in conjunction with JSPs and servlets to access SQL databases has also been a common practice for many years. DAOs were first introduced as a design pattern in the early 2000s, and since then, they have been widely adopted as a best practice.
The end result is a web application that can provide rich functionality to users while remaining easy to maintain and extend over time.
2 JSP: JavaServer Page
JavaServer Page (JSP) provides a simplified and fast mean to generate dynamic web contents.
It allows you to mix static HTML with dynamically generated HTML - in the way that the business logic and the presentation are well separated.
2.1 JSPs are Internally Compiled into Java Servlets
That is to say, anything that can be done using JSPs can also be accomplished using Java servlets.
However, it is important to note that servlets and JSPs are complementary technologies, NOT replacement of each other.
- Servlet can be viewed as HTML inside Java, which is better for implementing business logic - as it is Java dominant.
- JSP, on the other hand, is Java inside HTML, which is superior for creating presentation - as it is HTML dominant.
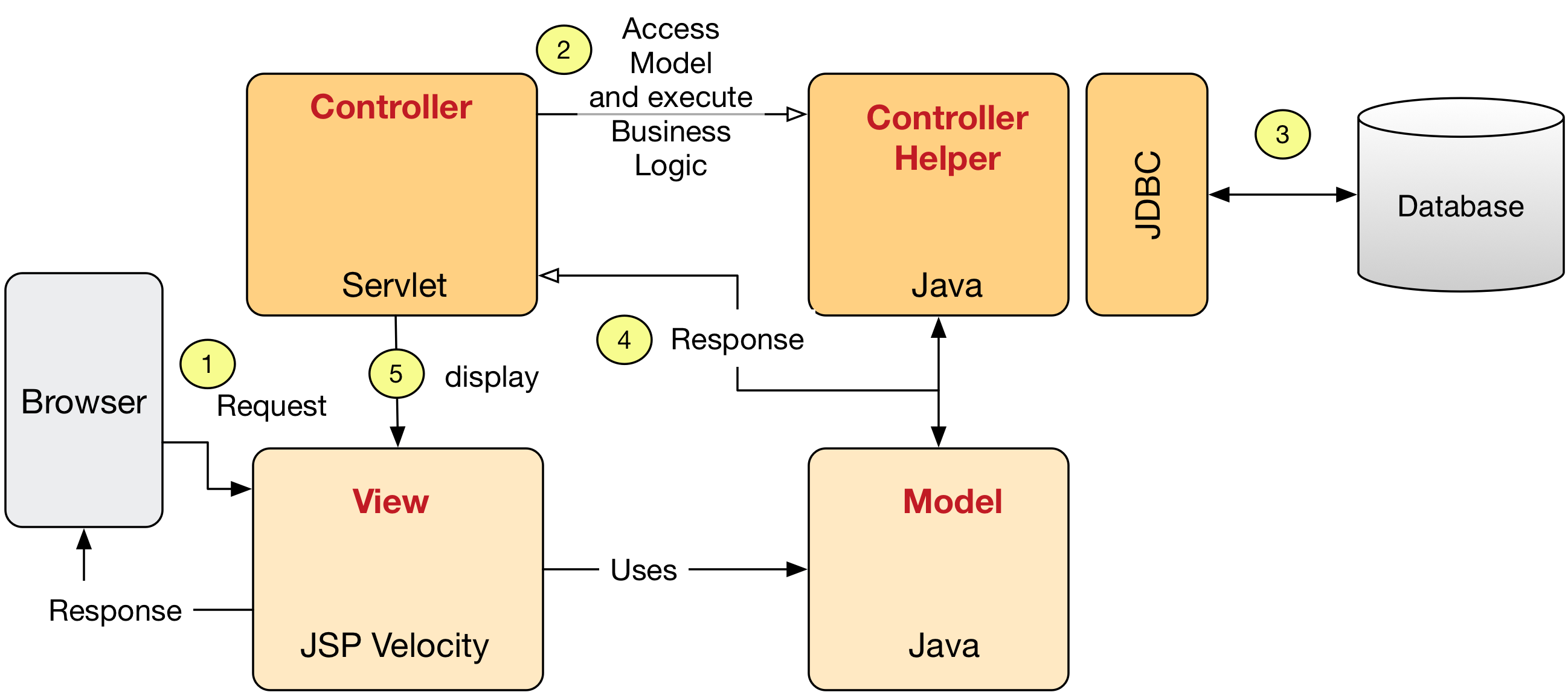
In a typical Model-View-Control (MVC) application:
- servlets are often used for the Controller (C), which involves complex programming logic.
- JSPs are often used for the View (V), which mainly deals with presentation.
- The Model (M) is usually implemented using JavaBean or EJB.
2.2 Apache Tomcat Server
JSPs, like servlets, are server-side programs run inside a HTTP server.
To support JSP/servlet, a Java-capable HTTP server is required.
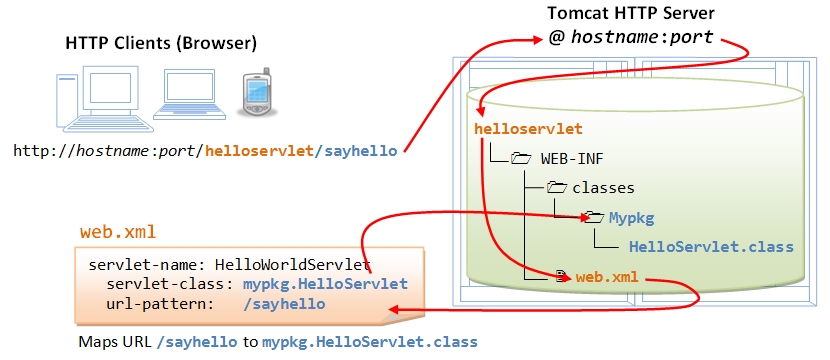
Tomcat Server is the official reference implementation (RI) for Java servlet and JSP, provided free by Apache.
2.3 Example: Java inside HTML
2.3.1 Code example
This JSP code generates a random number and displays a message to the user based on the value of the number.
If the number is greater than 0.95, the user is told they will have a lucky day, and if the number is less than or equal to 0.95, the user is told that life goes on.
DemoApplication.java
<html>
<head><title>First JSP</title></head>
<body>
<%
double num = Math.random();
if (num > 0.95) {
%>
<h2>You'll have a luck day!</h2><p>(<%= num %>)</p>
<%
} else {
%>
<h2>Well, life goes on ... </h2><p>(<%= num %>)</p>
<%
}
%>
<a href="<%= request.getRequestURI() %>"><h3>Try Again</h3></a>
</body>
</html>The random number is displayed along with the message, and the user is given the option to try again by clicking on a link that reloads the page.
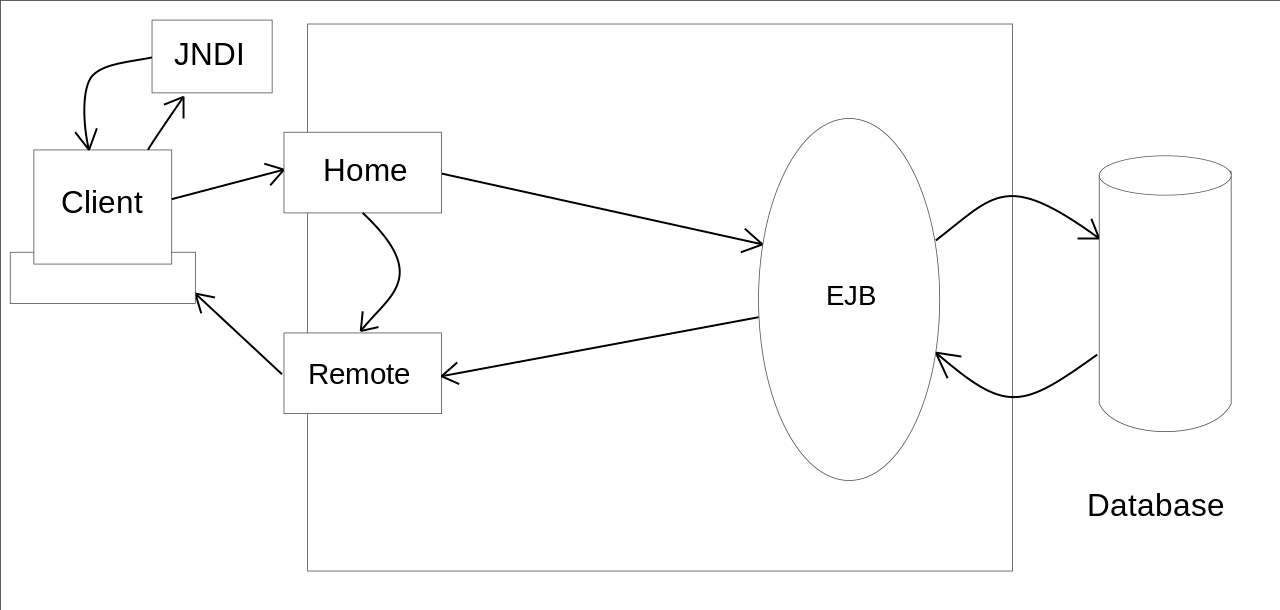
3 EJB: Enterprise JavaBeans
Enterprise JavaBeans (Enterprise JavaBeans) is one of several Java APIs for modular construction of enterprise software.
EJB is a server-side software component that encapsulates business logic of an application. An EJB web container provides a runtime environment for web related software components, including computer security, Java servlet lifecycle management, transaction processing, and other web services.
The EJB specification is a subset of the Java EE specification.
The EJB specification provides a standard way to implement the server-side (also called “back-end”) ‘business’ software typically found in enterprise applications (as opposed to ‘front-end’ user interface software). Such software addresses the same types of problem, and solutions to these problems are often repeatedly re-implemented by programmers.
Jakarta Enterprise Beans is intended to handle such common concerns as persistence, transactional integrity and security in a standard way, leaving programmers free to concentrate on the particular parts of the enterprise software at hand.
The following shows a basic example of what an EJB looks like in code:
CustomerService.java
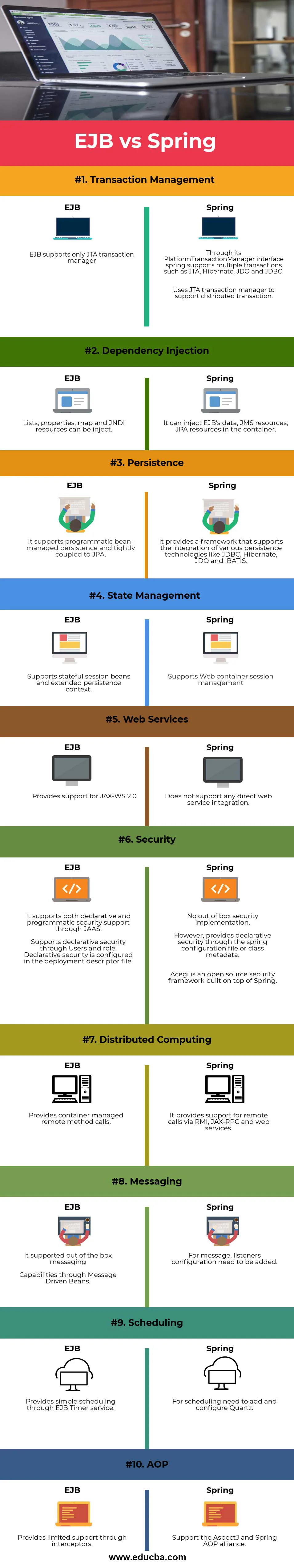
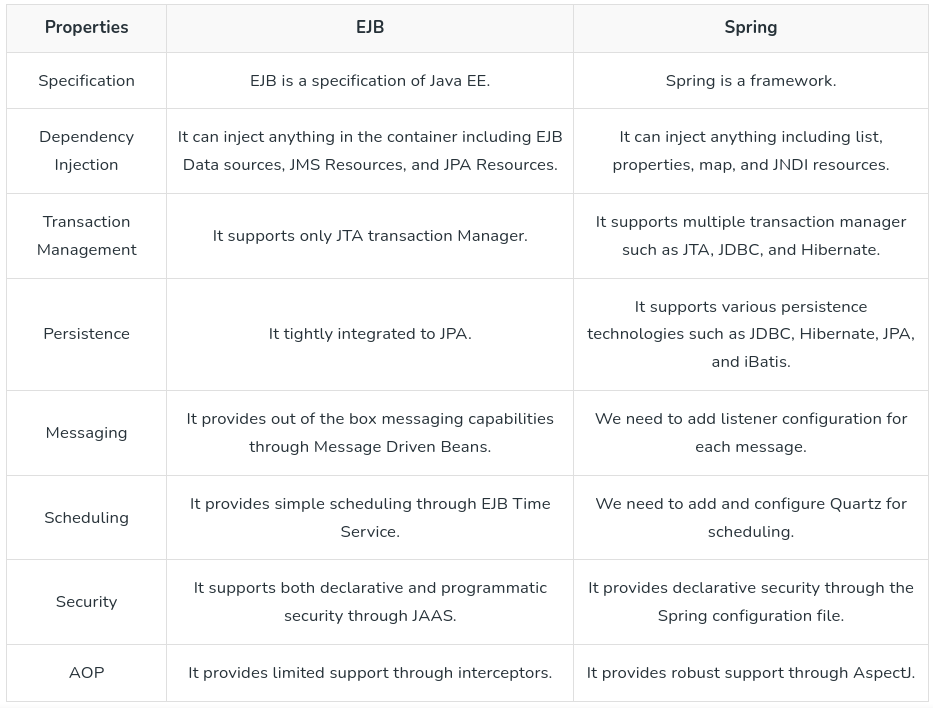
3.1 EJB vs Spring
EJB (Enterprise JavaBeans) and Spring are frameworks for developing enterprise applications in Java.
Both offer solutions for managing application components and facilitating enterprise-level features like transaction management and security. However, they differ in several key aspects.
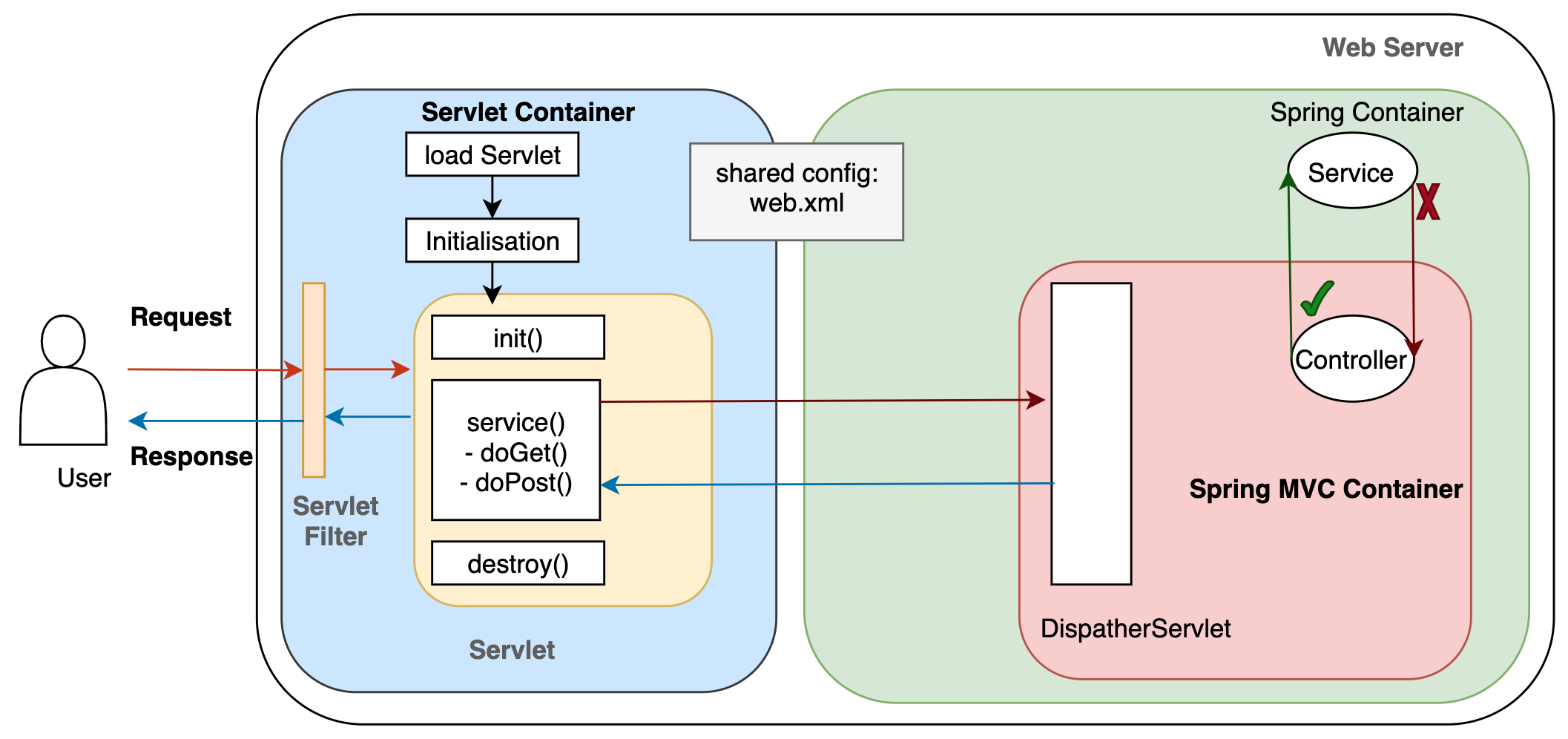
EJB is part of the Java EE platform, providing a standardized approach to building enterprise applications, while Spring is a lightweight and modular framework offering comprehensive support for dependency injection, aspect-oriented programming, and MVC architecture.
Spring promotes loosely coupled components and easier unit testing compared to EJB, which traditionally requires a full-fledged Java EE container for deployment.