React JS App: conditional render
ReactJS conditional render
1 Overview
📘 conditional render
React conditional rendering refers to the technique of rendering different components or elements in a React application based on certain conditions. This allows you to control the rendering of components based on the values of variables or the state of your application.
2 Basic conditional render
Your components will often need to display different things depending on different conditions.
Here’s an example of how you might use conditional rendering in a React component:
App.js
In this example, the MyComponent component uses an if statement to determine whether to render a “Loading…” message or a “Hello, world!” message, based on the value of the isLoading prop.
3 Ternary operator
You can also use the ternary operator ?: to conditionally render elements in a more concise way:
App.js
In this example, the ternary operator checks the value of the isLoading prop and returns a “Loading…” message if it is true, or a “Hello, world!” message if it is false.
Conditional rendering is a useful technique for controlling the rendering of components in a React application. It allows you to tailor the rendering of your application based on the state of your application or the values of variables.
4 Conditionally returning JSX
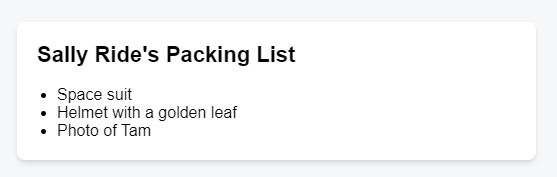
Let’s say you have a PackingList component rendering several Items, which can be marked as packed or not.
App.js
Notice that some of the Item components have their isPacked prop set to true instead of false. You want to add a checkmark (✔) to packed items if isPacked={true}.
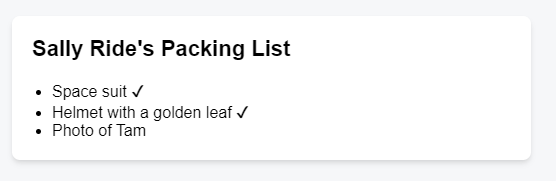
If the isPacked prop is true, this code returns a different JSX tree. With this change, some of the items get a checkmark at the end:
App.js
function Item({ name, isPacked }) {
if (isPacked) {
return <li className="item">{name} ✔</li>;
}
return <li className="item">{name}</li>;
}
export default function PackingList() {
return (
<section>
<h1>Sally Ride's Packing List</h1>
<ul>
<Item
isPacked={true}
name="Space suit"
/>
<Item
isPacked={true}
name="Helmet with a golden leaf"
/>
<Item
isPacked={false}
name="Photo of Tam"
/>
</ul>
</section>
);
}5 Example 1:
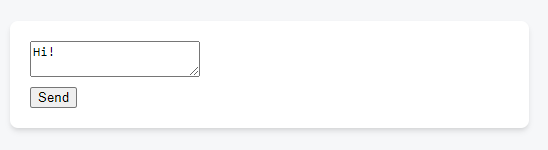
In this example, when you press send, setIsSent(true) tells React to re-render the UI:
App.js
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function Form() {
const [isSent, setIsSent] = useState(false);
const [message, setMessage] = useState('Hi!');
if (isSent) {
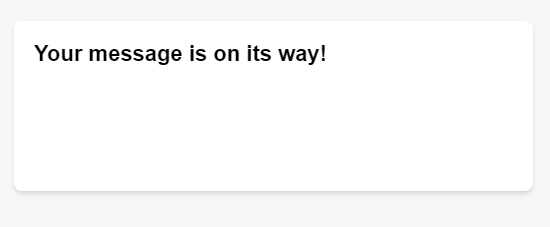
return <h1>Your message is on its way!</h1>
}
return (
<form onSubmit={(e) => {
e.preventDefault();
setIsSent(true);
sendMessage(message);
}}>
<textarea
placeholder="Message"
value={message}
onChange={e => setMessage(e.target.value)}
/>
<button type="submit">Send</button>
</form>
);
}
function sendMessage(message) {
// ...
}Here’s what happens when you click the button Send:
- The
onSubmitevent handler executes. setIsSent(true)setsisSenttotrueand queues a new render.- React re-renders the component according to the new
isSentvalue. - The new rendering with
isSenttotrueprints the first return (#7)
6 Example 2: crosswalk
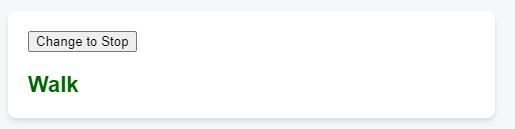
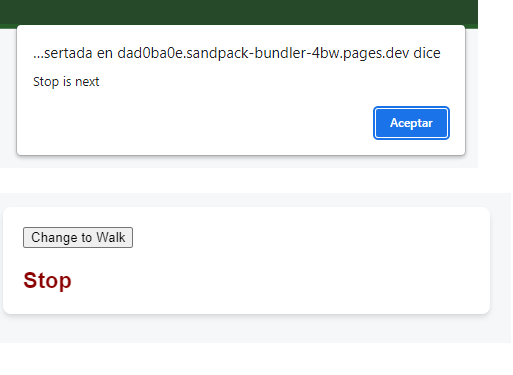
Here is a crosswalk light component that toggles on when the button is pressed:
App.js
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function TrafficLight() {
const [walk, setWalk] = useState(true);
function handleClick() {
setWalk(!walk);
alert(walk ? 'Stop is next' : 'Walk is next');
}
return (
<>
<button onClick={handleClick}>
Change to {walk ? 'Stop' : 'Walk'}
</button>
<h1 style={{
color: walk ? 'darkgreen' : 'darkred'
}}>
{walk ? 'Walk' : 'Stop'}
</h1>
</>
);
}