Lab#RE03-3: API Rest Mono
ReactJS labs
📘 React JS Lab#RE03-3: API Rest CRUD
A CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) Todo app with RESTful API integration:
- Using
AxiosandFetchAxiosandFetchare JavaScript libraries used for making HTTP requests to the API endpoints.AxiosorFetchcan be used to send HTTP requests to these endpoints, allowing data manipulation through CRUD operations.
- Fake server-side implemented with
MockAPI:- by utilizing
MockAPI, developers can create custom API endpoints to mimic server-side functionality.
- by utilizing
- The Todo app allows users to
create,read,update, anddeletetasks. - This integration will build a fully functional Todo application with API communication and data persistence.
1 Overview
From previous lab, we are going to persist data on server by API Rest using Axios (or fetch)`.
1.1 References:
1.1.1 Todo
2 mock api
MockAPI.iois a web service that allows developers to create and simulate RESTful APIs for testing and development purposes.
With MockAPI.io, developers can easily generate custom API endpoints and define the responses they want to receive when those endpoints are called. It provides a user-friendly interface to create, manage, and configure mock APIs, making it simple to simulate different scenarios and test how an application interacts with an API.
MockAPI.io supports various HTTP methods, request headers, query parameters, and response types, allowing developers to mimic real API behavior. It’s a valuable tool for rapid prototyping, integration testing, and mocking data during development.
3 axios
Axiosis a JavaScript library used for making HTTP requests in React applications.
It provides an easy-to-use and consistent API for performing asynchronous operations, such as fetching data from an API.
Axios supports features like interceptors, automatic request/response transformation, and error handling. It works both in the browser and Node.js environments and offers support for various request methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.).
Axios simplifies the process of making HTTP requests by providing a higher-level abstraction and allowing developers to handle responses and errors more efficiently.
4 fetch
Fetchis a built-in web API in modern browsers that allows making HTTP requests in React applications and other JavaScript environments.
It provides a native and low-level way of fetching resources from a server.
Fetch operates using Promises, enabling asynchronous operations and providing a more modern alternative to the older XMLHttpRequest (XHR) approach.
Fetch supports sending requests and receiving responses, but it lacks some advanced features provided by libraries like Axios, such as automatic request/response transformation and interceptors.
5 step-by-step todo api rest
5.1 General idea: schema
5.1.1 Components
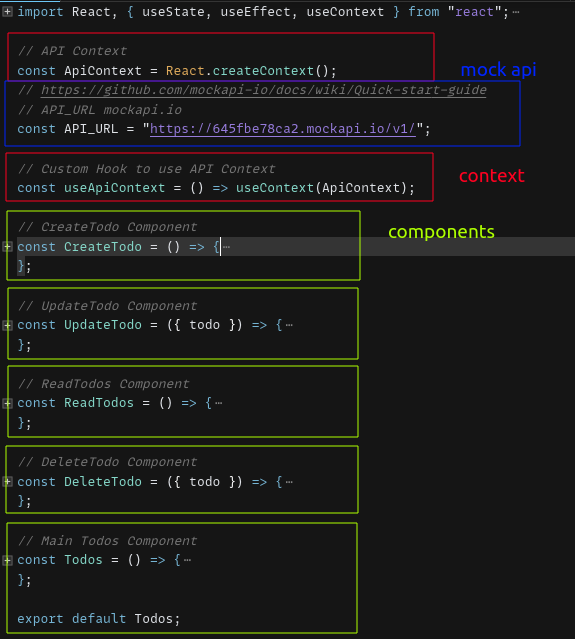
Let’s create first at all our core components:
- The
CreateTodocomponent is responsible for rendering a form to create a new Todo item. It uses React’s useState hook to manage the state of input fields. - The
UpdateTodocomponent displays a checkbox that represents the completion status of a Todo item. It receives the Todo object as a prop and handles the update of the completion status. - The
ReadTodoscomponent renders a list of Todo items fetched from an API. It uses React’s useState hook to manage the state of the Todo items. - The
DeleteTodocomponent displays a button to delete a Todo item. It receives the Todo object as a prop and handles the deletion.
The main
Todoscomponent is responsible for managing the state of all Todo items.
It fetches the Todo items from an API using the useEffect hook and stores them in the state using the useState hook.
It also provides the necessary functions to manipulate the Todo items through the ApiContext, which is created using React’s createContext hook:
addTodoupdateTododeleteTodofetchTodos
The ApiContext.Provider wraps these components to provide access to the Todo items and manipulation functions throughout the component tree.
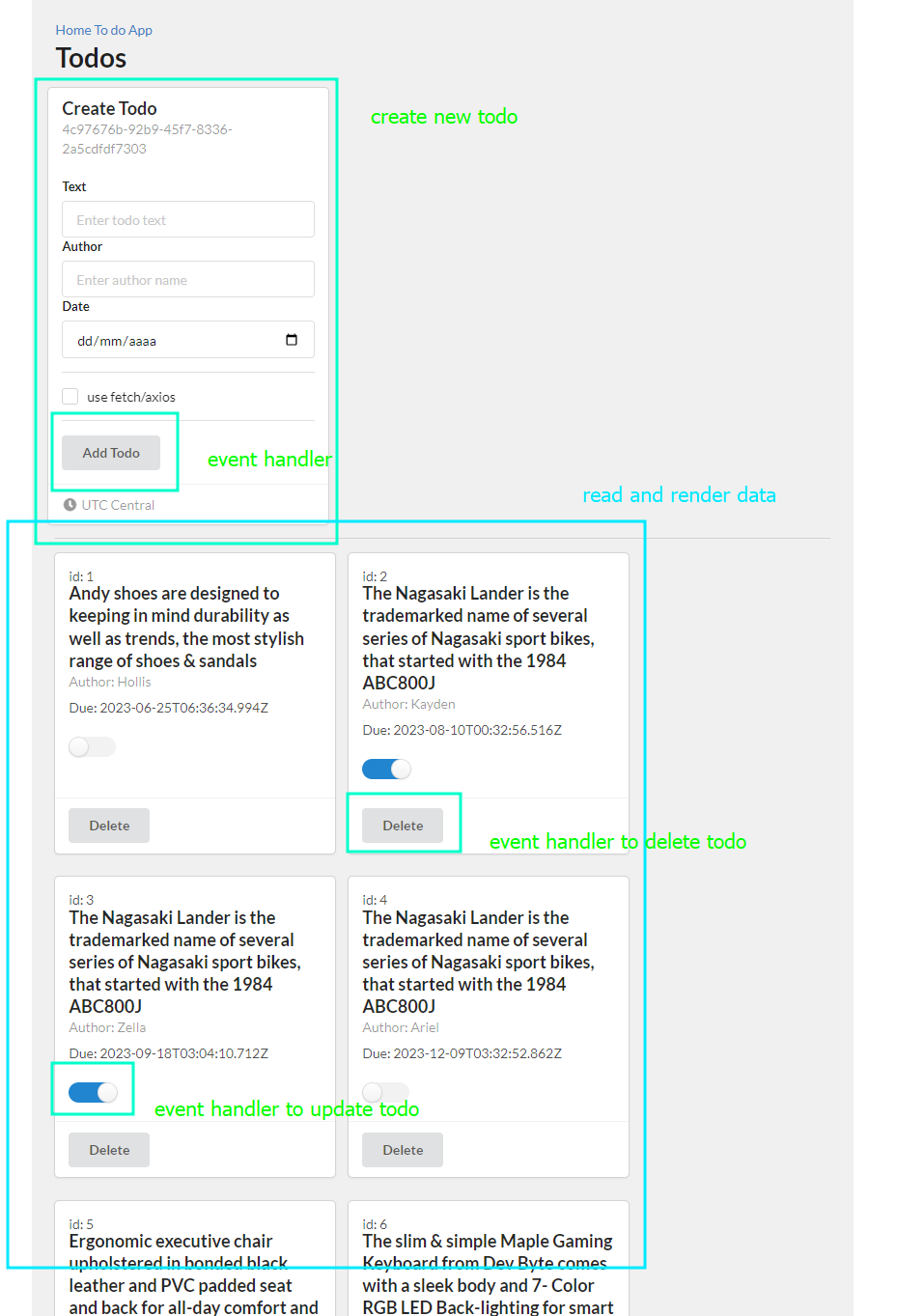
At the end, the main component Todos component renders the CreateTodo component and the ReadTodos component within a container.
ToDoGrid.jsx
import React, { useState, useEffect, useContext } from "react";
import {Container, Card, Checkbox, Button, Form, Divider,Icon }
from "semantic-ui-react";
import axios from "axios";
import { v4 as uuidv4 } from "uuid";
// https://github.com/mockapi-io/docs/wiki/Quick-start-guide
// API Context
const ApiContext = React.createContext();
// API_URL mockapi.io
const API_URL = "https://645fbe7.mockapi.io/v1/";
// Custom Hook to use API Context
const useApiContext = () => useContext(ApiContext);
// CreateTodo Component
const CreateTodo = () => {
const [text, setText] = useState("");
const [author, setAuthor] = useState("");
const [due, setDue] = useState("");
const { addTodo } = useApiContext();
// to-do
return (
<Form>
</Form>
);
};
// UpdateTodo Component
const UpdateTodo = ({ todo }) => {
// to-do
return (
<Checkbox toggle checked={todo.completed}
onChange={handleUpdateTodo} />
);
};
// ReadTodos Component
const ReadTodos = () => {
// to-do
return (
<Card.Group>
{todos.map((todo) => (
// to-do
))}
</Card.Group>
);
};
// DeleteTodo Component
const DeleteTodo = ({ todo }) => {
// to-do
return <Button onClick={handleDeleteTodo}>Delete</Button>;
};5.1.2 Axios and Main Component
Main component and Axios functions.
- We use the
ApiContext.Providercomponent to provide a context that includes the todos array, addTodo function, updateTodo function, and deleteTodo function to its child components. - The
todosstate is initialized as an empty array using theuseStatehook. - Axios functions:
fetchTodosretrieves todos from the API and sets them in the state.addTodosends a new todo to the API and updates the local state.updateTodotoggles the completed property of a todo.deleteTodoremoves a todo from the API and updates the state.
- The component renders child components within a Container component, including a:
heading,- a component for creating new todos (
CreateTodo), - a
divider, and - a component for reading/displaying existing todos (
ReadTodos).
ToDoGrid.jsx
// -------------------------------------------------------------
// Main Todos Component ----------------------------------------
//--------------------------------------------------------------
const Todos = () => {
const [todos, setTodos] = useState([]);
useEffect(() => {
fetchTodos();
}, []);
const fetchTodos = async () => {
// to-do
};
const addTodo = (newTodo) => {
// to-do
};
const updateTodo = async (id) => {
// to-do
};
const deleteTodo = async (id) => {
// to-do
};
return (
<ApiContext.Provider
value={{ todos, addTodo, updateTodo, deleteTodo }}>
<Container>
<h1>Todos</h1>
<CreateTodo />
<Divider />
<ReadTodos />
</Container>
</ApiContext.Provider>
);
};
export default Todos;5.1.3 context
We create a empty custom context called ApiContext using React.createContext().
ApiContext is used to provide data and functions related to todos to its child components.
The data and functions (todos, addTodo, updateTodo, deleteTodo) are passed as values to the ApiContext.Provider component.
This makes them accessible to any descendant component that consumes the ApiContext using the useContext hook.
5.1.4 async
The async function declaration declares an async function where the await keyword is permitted within the function body.
The async and await keywords enable asynchronous, promise-based behavior to be written in a cleaner style, avoiding the need to explicitly configure promise chains.
Async functions may also be defined as expressions.
References:
5.2 General idea: implemented
Code ToDoGrid.js uses this libreries and tools:
SemanticCSSAxiosApi Rest- Components
.jsx - React Hooks:
useState,useEffectanduseContext(as API Context custom) - uuidv4
- mockapi.io
- and NodeJS/npm
5.2.1 createContext
ToDoGrid.jsx
import React, { useState, useEffect, useContext } from "react";
import {
Container,
Card,
Checkbox,
Button,
Form,
Divider,
Icon
} from "semantic-ui-react";
import axios from "axios";
import { v4 as uuidv4 } from "uuid";
// https://github.com/mockapi-io/docs/wiki/Quick-start-guide
// API Context
const ApiContext = React.createContext();
// API_URL mockapi.io
const API_URL = "https://y45yh6y55dgfh.mockapi.io/v1/";
// Custom Hook to use API Context
const useApiContext = () => useContext(ApiContext);
//....| Line | Explanations |
|---|---|
const ApiContext = React.createContext(); |
Creates a new context object called ApiContext using the createContext, this context object will be used to share data and functions between components. |
const API_URL ="https://y45yh6y55dgfh.mockapi.io/v1/"; |
Sets the value of the constant API_URL to be the URL of a mock API. This URL is used to make HTTP requests and interact with the API in the application. |
const useApiContext = () => useContext(ApiContext); |
Defines a custom hook called useApiContext. This hook uses the useContext hook from React to retrieve the current value of the ApiContext. It provides a convenient way to access the context and its associated data and functions within components. |
5.2.2 CreateTodo
ToDoGrid.jsx
//....
// CreateTodo Component
const CreateTodo = () => {
const [text, setText] = useState("");
const [author, setAuthor] = useState("");
const [due, setDue] = useState("");
const { addTodo } = useApiContext();
const handleAddTodo = () => {
addTodo({
id: uuidv4(),
text,
author,
due
});
setText("");
setAuthor("");
setDue("");
};
return (
<Form>
<Form.Group>
<Card>
<Card.Content>
<Card.Header>Create Todo</Card.Header>
<Card.Meta>
<p>{uuidv4()}</p>
</Card.Meta>
<br />
<Form.Field>
<label>Text</label>
<input
type="text"
value={text}
onChange={(e) => setText(e.target.value)}
placeholder="Enter todo text"
/>
</Form.Field>
<Form.Field>
<label>Author</label>
<input
type="text"
value={author}
onChange={(e) => setAuthor(e.target.value)}
placeholder="Enter author name"
/>
</Form.Field>
<Form.Field>
<label>Date</label>
<input
type="date"
value={author}
onChange={(e) => setDue(e.target.value)}
placeholder="Enter author name"
/>
</Form.Field>
<Divider />
<Form.Field>
<Checkbox label="use fetch/axios" />
</Form.Field>
<Divider />
<Button onClick={handleAddTodo}>Add Todo</Button>
</Card.Content>
<Card.Content extra>
<a>
<Icon name="time" />
UTC Central
</a>
</Card.Content>
</Card>
</Form.Group>
</Form>
);
};
//....5.2.3 updateTodo
The line of code const { addTodo } = useApiContext(); is using the useApiContext custom hook to access the addTodo function from the API context.
const { addTodo } = useApiContext();
This line of code enables the component to call the addTodo function and utilize its functionality, such as adding a new todo item to the application’s state or performing any other actions associated with adding todos.
The useApiContext hook is a custom hook that internally uses the useContext hook from React. It allows components to access the values provided by the ApiContext.Provider higher up in the component tree.
By calling useApiContext, the component can retrieve the addTodo function from the API context.
The destructuring assignment { addTodo } extracts the addTodo function from the returned object, making it available for use within the component.
5.2.4 ReadTodos
ToDoGrid.jsx
// ReadTodos Component
const ReadTodos = () => {
const { todos } = useApiContext();
return (
<Card.Group>
{todos.map((todo) => (
<Card key={todo.id}>
<Card.Content>
<Card.Description>id: {todo.id}
</Card.Description>
<Card.Header>{todo.text}
</Card.Header>
<Card.Meta>Author: {todo.author}
</Card.Meta>
<Card.Description>Due: {todo.due}
</Card.Description>
<br />
<UpdateTodo todo={todo} />
</Card.Content>
<Card.Content extra>
<DeleteTodo todo={todo} />
</Card.Content>
</Card>
))}
</Card.Group>
);
};
//....5.2.5 DeleteTodo
5.2.6 Main component: Todos
Main component and Axios implemented functions:
- The
fetchTodosfunction is called when the component mounts, which retrieves todos from an API endpoint using axios and sets the todos in the state. - The
addTodofunction sends a new todo object to the API endpoint using a POST request and updates the local todos state with the new todo. It also handles error cases. - The
updateTodofunction toggles the completed property of a todo item with a given id by sending a PUT request to the API endpoint and updating the local todos state accordingly. - The
deleteTodofunction deletes a todo item with a given id by sending a DELETE request to the API endpoint and updates the local todos state by filtering out the deleted todo.
ToDoGrid.jsx
// Main Todos Component
const Todos = () => {
const [todos, setTodos] = useState([]);
useEffect(() => {
fetchTodos();
}, []);
const fetchTodos = async () => {
try {
const response =
await axios.get(`${API_URL}/todo`);
setTodos(response.data);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
};
const addTodo = (newTodo) => {
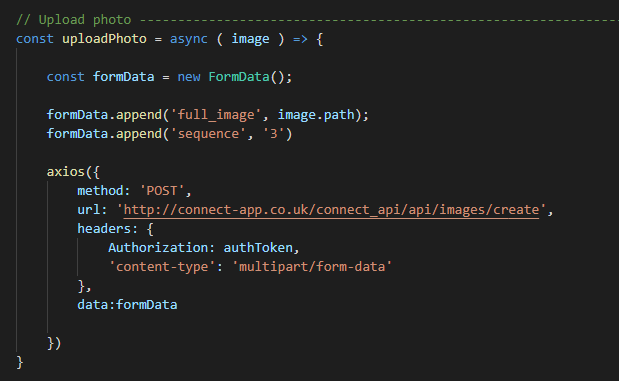
fetch(`${API_URL}/todo/`, {
method: "POST",
headers: { "content-type": "application/json" },
// Send your data in the request body as JSON
body: JSON.stringify(newTodo)
})
.then((res) => {
setTodos([...todos, newTodo]);
const response = {};
if (response.ok) {
return response.json();
}
// handle error
})
.then((task) => {
// do something with the new task
})
.catch((error) => {
// handle error
});
};
const updateTodo = async (id) => {
try {
const updatedTodos = todos.map((todo) => {
if (todo.id === id) {
return { ...todo, completed: !todo.completed };
}
return todo;
});
await axios.put(`${API_URL}/todo/${id}`, updatedTodos);
setTodos(updatedTodos);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
};
const deleteTodo = async (id) => {
try {
await axios.delete(`${API_URL}/todo/${id}`);
const filteredTodos =
todos.filter((todo) => todo.id !== id);
setTodos(filteredTodos);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
};
return (
<ApiContext.Provider
value={{ todos, addTodo, updateTodo, deleteTodo }}>
<Container>
<h1>Todos</h1>
<CreateTodo />
<Divider />
<ReadTodos />
</Container>
</ApiContext.Provider>
);
};
export default Todos;The context enables the sharing of todos data and related functions across multiple components without the need for prop drilling.
The CreateTodo component uses the useApiContext custom hook to access the addTodo function from the context. It allows users to create a new todo and calls the addTodo function to add the new todo to the list.
Similarly, the UpdateTodo component uses the useApiContext hook to access the updateTodo function from the context. It provides a checkbox to toggle the completion status of a todo.
The ReadTodos component uses the useApiContext hook to access the todos array from the context. It displays the existing todos and provides the ability to update and delete them.
5.3 Creating domains: decoupling
References:
Before coding it let’s discuss the right approach to work it with domains at next lab, Lab#RE03-4.
6 Versions
| Code Version | Commit | Folder-Tree | Screeshoots |
|---|---|---|---|
| todoApp 0.3 | add ToDoGrid component to project: todoApp 0.3 | initial tree-folder | render todoGrid |