classDiagram
class MenuManager {
- menus: HashMap<String, Menu>
- qty: int
- size: double
- lastModified: Date
+ addMenu(menu: Menu, data: String): void
+ updateMenu(): void
+ deleteMenu(title: String): void
+ getMenu(title: String): Menu
+ getMenus(): List<>
+ rateMenu(rate: int, menu: Menu): void
+ saveToCSV(): void
+ deleteCSV(): void
}
Lab#SB08-1: Restaurant UML
Spring Boot Restaurant Management DDD and UML
📘 Spring Boot Lab#SB00-1: Restaurant UML We are going to evolve the current Java SE Restaurant project into a Spring Boot RestaurantManagement System with an H2 DB and web interface using Thymeleaf/Vaadin.
The resulting
Spring Boot Projectwould be similar to the currentJava SE Restaurant Project, with the addition of the Spring Bootannotationsand theH2 databaseconfiguration.
The classes (such as
Booking,Menu,Table,Customer, and the variousOrderclasses) would be annotated with the @Entity annotation to indicate that they are persistent entities, and the repositories would be annotated with the @Repository annotation.
The services would be annotated with the @Service
annotation, and the controllers would be annotated with the @Controller annotation.
The
Thymeleaftemplates would be created in theresources/templatesfolder of the project. These templates would include views for managing bookings, menus, tables, customers, and different types of orders (TakeAway, Shipping, and EatIn).
This Spring Boot version of the RestaurantManagement System would provide a robust, database-backed web application for managing all aspects of a restaurant’s operations, from bookings and menu management to order processing and customer interactions.
1 From RestaurantProject to RestaurantManagement
1.1 Create a new Spring Boot project & H2 DB
Create a new Spring Boot project: The first step would be to create a new Spring Boot project in the preferred IDE or text editor.
The project can be created using Spring Initializr, which will create the necessary file structure and dependencies.
1.2 Model & Entities
Create a Menu Entity: To represent a menu item in the restaurant management system, create a Menu @Entity
It could include attributes such as name, price, description, category (appetizer, main course, dessert, etc.), and availability status.
Create a Customer Entity: To represent a customer in the system, create a Customer entity that includes attributes such as customer ID, name, phone number, email, and reservation history.Create Booking Entity: To represent a booking in the system, create a Booking entity that includes attributes such as booking date, time, number of people, tables, and associated customer.Create Staff Entity: To represent staff members in the system, create a Staff entity that includes attributes such as staff ID, name, position, shift schedules, and assigned tables.
1.3 Domains: @Controller, @Service and @Repository
Create Repositories: To access the data stored in the database, create repositories for each entity. The repositories will provide the methods to create, read, update, and delete the data.Create Services: Create services that will implement the business logic of the system by calling the repository methods.
The services will provide the methods to search for available tables, make a reservation, update menu items, process orders, manage staff schedules, handle customer feedback, and generate reports on restaurant performance.
Create Controllers: Create controllers that will handle the HTTP requests from the web interface by calling the service methods.
The controllers will provide the methods to create a customer account, search for available tables, make a reservation, view and update menu items, place an order, manage staff schedules, submit customer feedback, and generate various reports.
2 MockUp
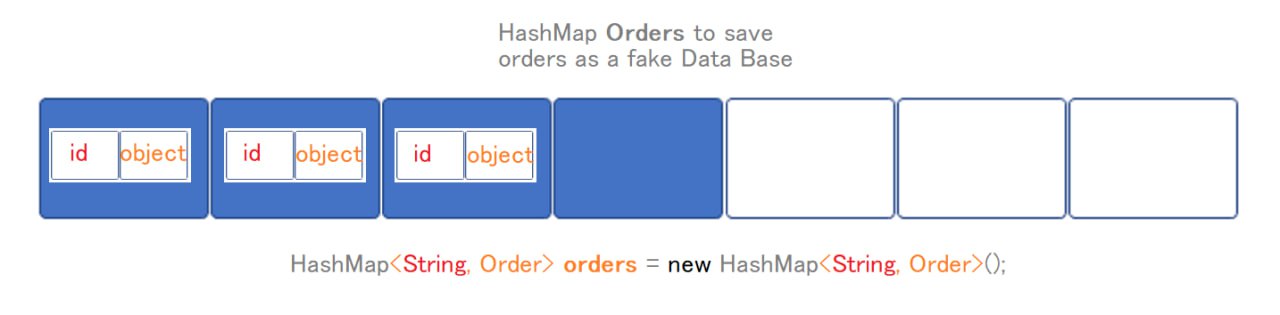
3 Fake DataBase: HashMaps
To start and test our UML we are goint to use HashMaps as a fake database.
Keep in mind that in more recent versions of Java, you can use the diamond operator (<>) to infer the generic types, making the declaration more concise:
HashMap<String, Order> orders = new HashMap<>();
Here’s what each part of the code means:
HashMap<String, Order>: This declares a newHashMapwith keys of typeStringand values of typeOrder. In other words, it’s a mapping from strings toOrderobjects.orders: This is the name of the variable that will reference theHashMap. You can choose any valid identifier as the variable name.= new HashMap<String, Order>();: This part of the code creates a new instance ofHashMapand assigns it to the variableorders. Thenewkeyword is used to allocate memory for theHashMap, and the<>syntax specifies the types of keys and values for theHashMap. In this case, keys are of typeString, and values are of typeOrder.
3.1 Entities Manager
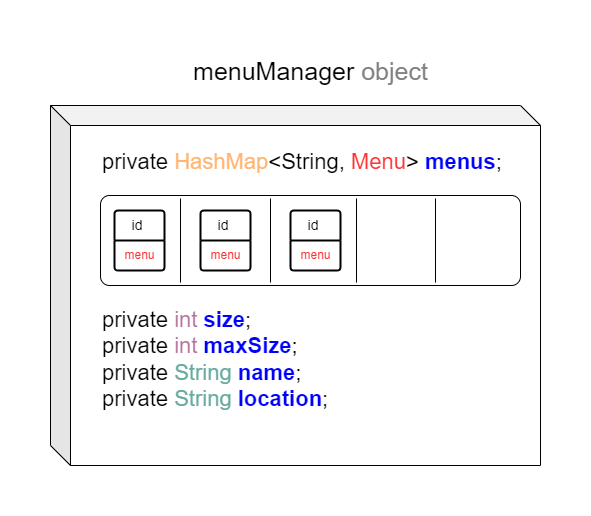
MenuManager
The MenuManager acts as a central hub for menu-related operations, promoting efficient management and systematic handling of menu entities in Java applications.
4 Discussion Solving: UML
Basic UML Java SE with restaurantDB Hashmap
Inhrence Order Spring Boot implementation