Python: Higher-order Functions
Python Higher-order Functions
1 Overview
📘 Higher-order functions in Python
Higher-order functions in Python are functions that either take other functions as arguments, return functions as their result, or both. They are a fundamental concept in functional programming, enabling the creation of more modular, flexible, and reusable code by allowing functions to be treated as first-class citizens.
These functions serve as a powerful abstraction tool since they facilitate dynamic behavior, such as applying different functions to data, generating new functions on-the-fly, or combining multiple functions in various ways. They can manipulate and operate on other functions, allowing for more expressive and concise code structures, and can be stored in variables, data structures, or used as return values from other functions.
In practical terms, higher-order functions support operations like function composition, function chaining, and conditional function application, all of which contribute significantly to code clarity and efficiency. Examples include functions that accept other functions as parameters to define custom behaviors or those that generate new functions based on specific input parameters, thus enabling flexible and dynamic programming patterns.
Overall, the power of higher-order functions stems from their ability to abstract over actions and behaviors, leading to code that is more modular, transparent, and adaptable to various programming tasks.
2 Higher-order Functions
- They are functions that take functions as arguments and/or return a function.
- Example of function that takes a function as an argument:
- Example of function that takes a function as an argument:
- Example of function that returns a function:
- Example of function that returns a function:
3 Lambdas
- Also known as lambda functions.
- Defined with the
lambdakeyword. - Small, anonymous functions.
- Specially useful for higher-order functions (next slides).
- Syntax:
lambda arguments: expression - The
expressionreturns by default.
100
Hello, Bob! You are 23 years old.
- We said lambda functions do not have names
- But we are “naming” them by using the
squareandgreetvariable names. - This is just for the sake of the example.
- If writting clean code, we prefer this, not lambdas:
4 What Are Lambdas Useful For Then?
- Perfect with higher-order functions.
- Defined in a single line and without a name.
- Ideal when the function is not reused anywhere else.
- Think of them as:
funciones de usar y tirar.
5 Python’s Higher-Order Functions
- Common higher-order functions in Python:
sorted(),max(),map(),reduce(),filter()…
5.1 Sorted
- The
sorted()function has an optionalkeyparameter. - It lets you customize the sort order by providing a function that returns a value to use for sorting purposes.
5.1.1 Example 1: Sorting a List of Dictionaries
- This crashes, as python cannot compare inequalities between dictionaries:
- Using the
keyparameter insorted().
5.1.2 Example 2: Sorting a List of Tuples
- Or in reverse order using the
reverseoptional parameter:
- How does this sort the data if we set
x[0]instead ofx[1]in the lambda?
- How does this sort the data if we set
x[0]instead ofx[1]in the lambda?
- Without lambdas things would be less comfortable (but doable).
5.1.3 Example 3: Sorting by Length of Strings
- Equivalently, we could omit the lambda entirely:
6 Max
- By default, max of alphabetical order (the last one):
- Accepts
keyargument. - Maximum in terms of length:
7 Map
- Applies a given function to each item in a sequence.
- Returns an iterable (a map object).
- You can convert the map object to a list or tuple if needed.
- Syntax:
map(function, sequence) - Converting to a list:
list(map(function, sequence)) - Traditionally, for applying a function to each element we use a
forloop.
- Using
map():
- Or we could also use the
doublerfunction if it is already defined:
8 Filter
- Filters the elements in a sequence based on a given function that returns a boolean value.
- Keeps the elements for which the function returns
Trueand discards the others.
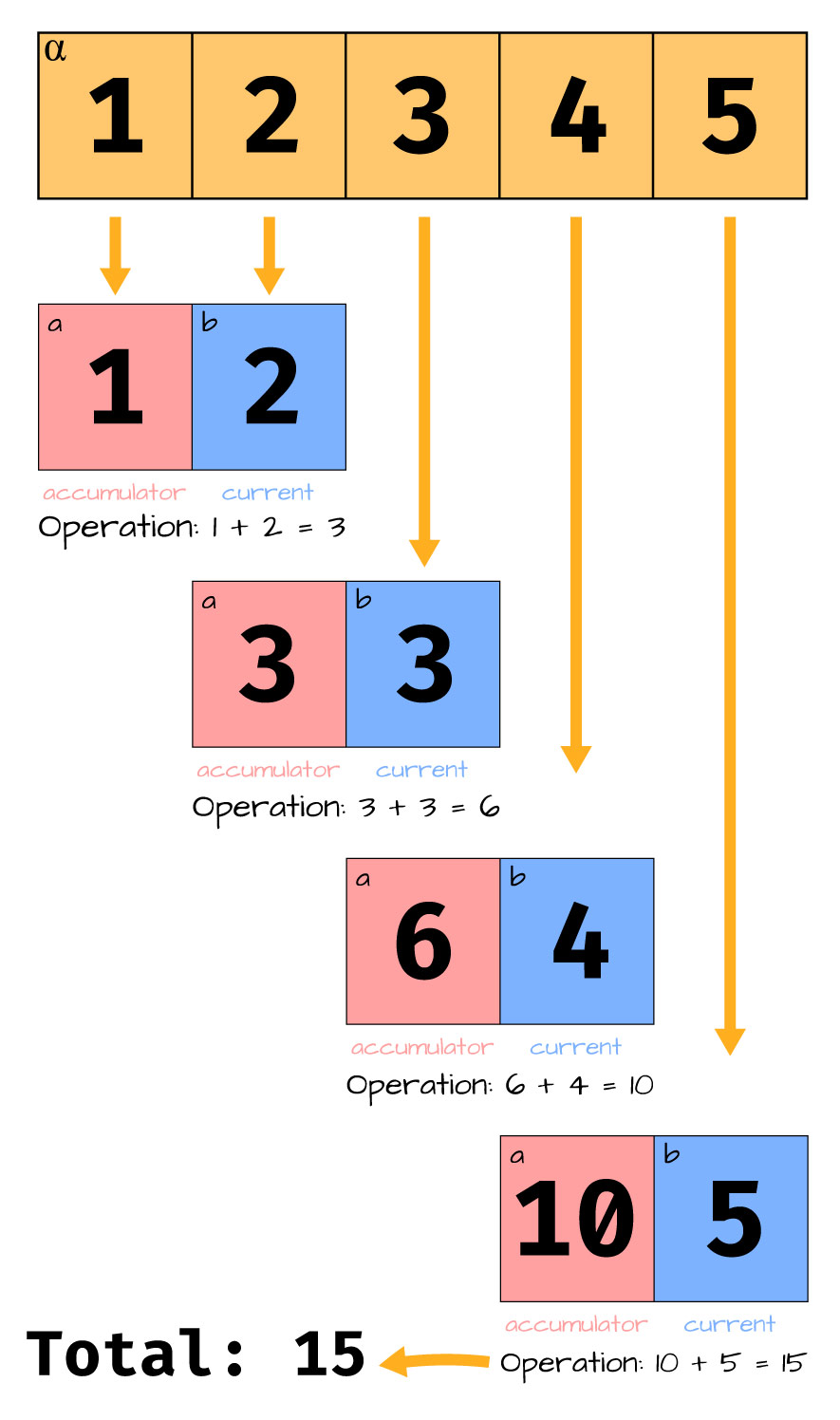
9 Reduce
- The
reducefunction is part of thefunctoolsmodule. - Applies a given function cumulatively to the items in a sequence from left to right.
- Reduces the sequence to a single value.
10 Exercises
10.1 Map
What is printed?
What is printed?
10.2 Filter
What is printed?
Filter all the prime numbers from a given integer list. You can use a function implemented for checking if a given number is prime or not.
10.3 Reduce
What is printed?
What is printed?
Use the reduce function from the functools module to find the longest word in a list of words. If there are multiple words with the same length, any of those words is fine.
10.4 Combinations
Get the squared elements of a list, but only include those whose square results in an odd number. Use map() and filter() functions to solve this problem.