DevOps: Introduction
DevOps what it is
📘 DevOps
DevOps is a cross-disciplinary community of practice dedicated to the study of building, evolving and operating rapidly-changing resilient systems at scale.
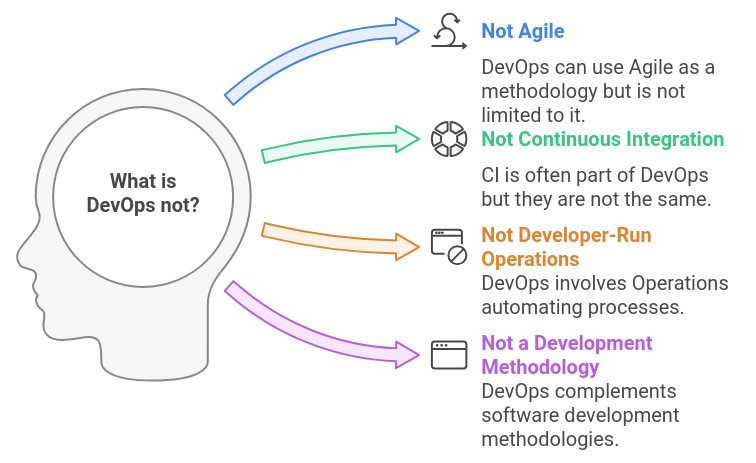
1 What DevOps Isn’t
Given that DevOps is a philosophy… a management approach… and the combination of multiple IT disciplines… it might be easier to quickly look at some of what it isn’t.
DevOps is not Agile. That said, your teams might indeed use Agile as a development methodology within an overall DevOps-style approach. Agile is certainly DevOps-compatible, and, like DevOps, values short, continual improvement.
DevOps is not Continuous Integration. That said, CI is often a part of DevOps-style behavior. The two can be really closely related, in fact - so closely that it’s hard to tell the difference. I suppose you could argue that it’s difficult to practice the DevOps philosophy without using CI as an enabling implementation, but you can definitely have CI without behaving like a DevOps organization, so the two aren’t exactly the same thing.
DevOps isn’t “the developers running Operations.” If anything, it’s Operations automating things to the point where Operations runs itself in response to authorized actions taken by other roles, including developers.
DevOps isn’t a software development methodology. See the first bullet, above. DevOps is what happens while software development is happening, and largely what happens when software development (or a cycle of it), is done. You still need to manage your software development - you just need to use a methodology that’s DevOps-compatible.
DevOps is not automation. However, you can’t have DevOps without automation. Automation is perhaps the biggest thing that Operations brings to the DevOps table, in fact.
Further, it actually seems to be an unstated goal of many DevOps champions to avoid the creation of any kind of trademarked, rigid, rulebook of “how to do DevOps,” as ITIL or TQM or something. This book certainly doesn’t attempt to provide “rules;” the goal here is to provide some understanding of what DevOps’ broad goals are.
2 What Is DevOps?
DevOps is a new term emerging from the collision of two major related trends.
- The first was also called “agile infrastructure” or “agile operations”; it sprang from applying Agile and Lean approaches to operations work.
- The second is a much expanded understanding of the value of collaboration between development and operations staff throughout all stages of the development lifecycle when creating and operating a service, and how important operations has become in our increasingly service-oriented world (cf. Operations: The New Secret Sauce).
One definition Jez Humble proposed to me is that
DevOpsis “a cross-disciplinary community of practice dedicated to the study of building, evolving and operating rapidly-changing resilient systems at scale.”
What Is DevOps by the agile admin
DevOps is a software development methodology that accelerates the delivery of higher-quality applications and services by combining and automating the work of software development and IT operations teams.
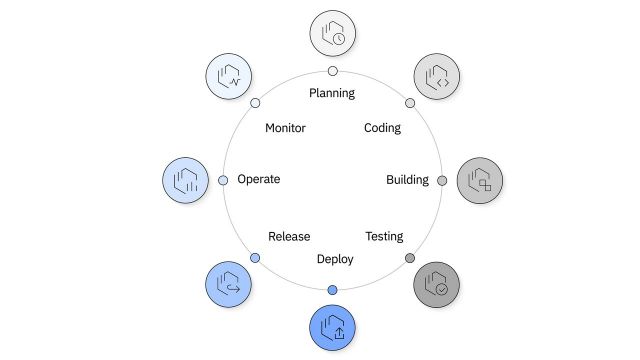
2.1 DevOps lifecycle
The DevOps lifecycle (sometimes called the continuous delivery pipeline, when portrayed in a linear fashion) is a series of iterative, automated development processes, or workflows, run within a larger, automated and iterative development lifecycle, designed to optimize the rapid delivery of high-quality software.
Workflow names and the number of workflows differ depending on whom you ask, but they often include these eight steps.
3 DevOps vs Site Reliability Engineering (SRE)
In the world of software development and IT operations, DevOps and Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) have emerged as critical methodologies for delivering high-quality, reliable software solutions.
While often used interchangeably, these approaches have distinct characteristics and goals that help organizations streamline their software delivery and maintenance processes.
DevOps and SRE are not competing methodologies but complementary approaches that can be integrated to create a robust, efficient software delivery and maintenance strategy.
While DevOps focuses on breaking down silos between development and operations, fostering collaboration and continuous delivery, SRE applies software engineering principles to operational challenges, ensuring system reliability and performance.
3.1 Comparison Table
The integration of these approaches allows organizations to balance rapid innovation with system stability:
DevOpsdrives the acceleration of software development and deployment, creating flexible and responsive delivery pipelines.SREcomplements this by implementing rigorous monitoring, establishing service level objectives, and creating systematic approaches to managing system reliability.
| Aspect | DevOps | SRE |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Continuous integration and delivery | System reliability and performance |
| Key Objective | Reduce barriers between development and operations | Maintain system reliability through engineering practices |
| Main Metrics | Deployment frequency, lead time, change failure rate | Service Level Indicators (SLIs), Error Budgets |
| Team Composition | Cross-functional teams | Specialized reliability engineers |
| Automation Level | High automation of delivery pipeline | Automation of operational tasks and monitoring |
| Change Management | Frequent, incremental changes | Controlled, measured changes |
| Cultural Approach | Collaborative, shared responsibility | Data-driven, systematic |
Where DevOps emphasizes cultural transformation and collaborative workflows, SRE provides a more quantitative framework for understanding system performance. By combining their strengths, teams can create automated, efficient processes that not only deliver software quickly but also maintain high standards of reliability and performance.
The synergy between
DevOpsandSREenables organizations to respond more effectively to technological challenges, reduce operational complexity, and create more resilient software systems. Rather than competing, these methodologies work together to address the complex demands of modern software development and infrastructure management.
Core Principles
- DevOps emphasizes:
- Continuous integration
- Rapid deployment
- Collaboration
- Automation of build and release processes
- SRE focuses on:
- Reliability engineering
- Performance optimization
- Proactive monitoring
- Error budget management
When to Use Each Approach
- Choose DevOps when:
- Needing to break down silos
- Wanting to accelerate software delivery
- Seeking to improve collaboration
- Choose SRE when:
- Requiring high system reliability
- Managing complex, large-scale systems
- Needing systematic approach to operational challenges