classDiagram
class Movie {
- title: String
- director: String
- genre: String
- size: double
+ Movie(title: String, director: String, genre: String, size: double)
+ getTitle(): String
+ getDirector(): String
+ getGenre(): String
+ getSize(): double
+ setDirector(director: String)
+ setGenre(genre: String)
+ setSize(size: double)
}
Lab#SE02-4: Movie/Review, interactivity and coupling
Java SE Lab 02
📘 Linux Lab#LI02-4: interactivity and coupling
After having a good approach with the labs done previously and from that point, having in mind the core-entity model and somemanagement/controller, let’s step up.
Add some interactivity through console with the user building on these new features and classes:
Import class Scanner:
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);A
while (true)loop with theCRUDoptions would be a nice idea.Work as simple as possible, just 3 classes, let s try to understand the problem:
MovieManagerMovieandMovieController
Propose some improvements.
What about coupling? Is tight or loose coupled, this code?
1 Java User Input (Scanner)
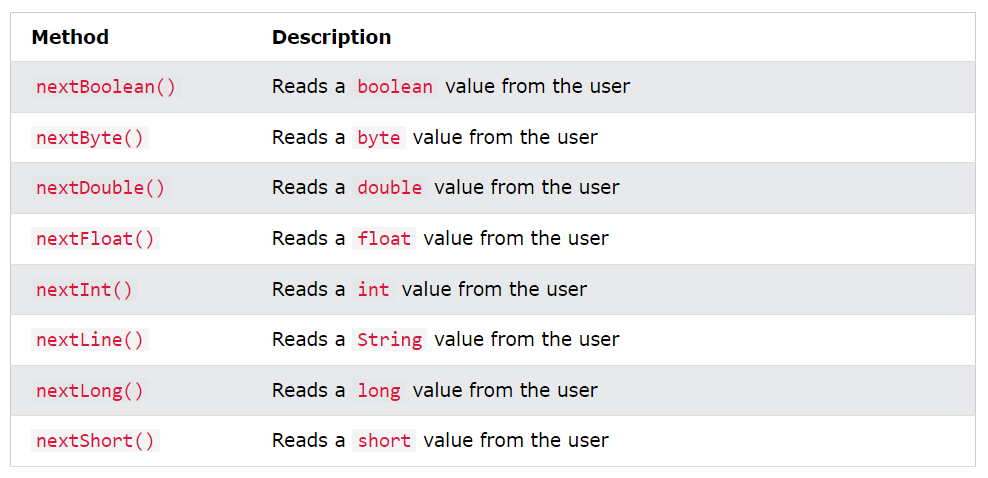
The Scanner class is used to get user input, and it is found in the java.util package.
To use the Scanner class, create an object of the class and use any of the available methods found in the Scanner class documentation.
In the example above, we used the nextLine() method, which is used to read Strings. To read other types, look at the table below:
2 Birding
Before coding, study this very basic example and check how it could grow:
- First Version: Birding 1.0
3 Core classes
You could then use these:
MovieController.java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MovieController {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("Please select an option:");
System.out.println("1. Add a movie");
System.out.println("2. Update a movie");
System.out.println("3. Delete a movie");
System.out.println("4. Get a movie by title");
System.out.println("5. Exit");
int option = scanner.nextInt();
if (option == 1) {
System.out.println("Enter the movie title:");
String title = scanner.next();
System.out.println("Enter the movie director:");
String director = scanner.next();
System.out.println("Enter the movie genre:");
String genre = scanner.next();
System.out.println("Enter the movie size:");
double size = scanner.nextDouble();
MovieManager.addMovie(title, director, genre, size);
System.out.println("Movie added successfully!");
} else if (option == 2) {
System.out.println("Enter the movie title:");
String title = scanner.next();
System.out.println("Enter the new movie director:");
String director = scanner.next();
System.out.println("Enter the new movie genre:");
String genre = scanner.next();
System.out.println("Enter the new movie size:");
double size = scanner.nextDouble();
MovieManager.updateMovie(title, director, genre,size);
System.out.println("Movie updated successfully!");
} else if (option == 3) {
System.out.println("Enter the movie title:");
String title = scanner.next();
MovieManager.deleteMovie(title);
System.out.println("Movie deleted successfully!");
} else if (option == 4) {
System.out.println("Enter the movie title:");
String title = scanner.next();
Movie movie = MovieManager.getMovie(title);
if (movie != null) {
System.out.println("Title: " + movie.getTitle());
System.out.println("Director: " + movie.getDirector());
System.out.println("Genre: " + movie.getGenre());
System.out.println("Size: " + movie.getSize());
} else { System.out.println("Movie not found!");}
} else if (option == 5) {
break;
} else {
System.out.println("Invalid option!");
}
}
scanner.close();
}
}In this diagram, the Movie class has the following properties: title, director, genre, and size, each with corresponding getters and setters. It also has a constructor that takes 4 parameters.
The MovieManager class has a HashMap of movies that stores Movie objects, an int variable qty that holds the number of movies stored in the manager, a double variable size that holds the total size of all the movies, a variable lastModified of type Date that holds the last date when a movie is added or deleted, and has several static methods which are addMovie, updateMovie, deleteMovie, getMovie, saveToCSV, deleteCSV which are CRUD operation over movies.
classDiagram
class MovieManager {
- movies: HashMap<String, Movie>
- qty: int
- size: double
- lastModified: Date
+ addMovie(title: String, director: String, genre: String, size: double): void
+ updateMovie(title: String, director: String, genre: String, size: double): void
+ deleteMovie(title: String): void
+ getMovie(title: String): Movie
+ saveToCSV(): void
+ deleteCSV(): void
}
The MovieController class has a main method which contains a loop that interacts with the user to perform CRUD operations on the Movie class using the static methods in the MovieManager class.
classDiagram
class MovieController {
+ main(args: String[]): void
}
4 Create static methods
MovieController.java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MovieController {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
MovieManager movieManager = new MovieManager();
while (true) {
String command = ask(scanner, "Option?");
if (command.equals("Quit")) {
break;
} else if (command.equals("Add")) {
add(scanner,movieManager);
} else if (command.equals("Delete")) {
delete(scanner,movieManager);
} else if (command.equals("Get")) {
get(scanner,movieManager);
} else if (command.equals("Update")) {
update(scanner,movieManager);
} else if (command.equals("Showall")) {
showall(scanner,movieManager);
} else {
System.out.println("Unknown command!");
}
}
}
public static String ask(Scanner input, String option) {
return null;
}
public static void add(Scanner input, MovieManager movieManager) {
}
public static void delete(Scanner input, MovieManager movieManager) {
}
public static void get(Scanner input, MovieManager movieManager) {
}
public static void update(Scanner input, MovieManager movieManager) {
public static void showall(Scanner input, MovieManager movieManager) {
}
}
}5 Grow your code
- Zero Sprint/Version:
- Meeting rules
- Roles: ScrumMaster, Product Owner, Specialist, Team
- Tech fundamentals: os, git
- Mockup: figma
- Documentation: obsidian, quarto
- Digital tools: github, gitlab, openProject, nextCloud
- UML: use-case, clas diagram, sequencial
- Core Project classes
- Product draft definition
- User stories, epics, tasks
- Product Backlog, Sprint 1 Backlog
- Sprint/Versions calendar
- Never, never, ever use Sprint Zero notation: it is a sin
- First Sprint/Version:
- Just basic Core classes, Model: Birding v1.0
- Second Sprint/Version:
- Starting to work in
mainand thinking (that is, create some new classes) in Domains
- Starting to work in
- Third Sprint/Version:
- Some improvements in organize clases,
Menu,MenuOptions,Utils: Birding v3.0
- Some improvements in organize clases,
- Fourth Sprint/Version:
- Start with MVC pattern: problems with
coupling
- Start with MVC pattern: problems with
- Fifth Sprint/Version:
- MVC implemented: Birding v5.0
- Sixth Sprint/Version:
- Add singleton and factory pattern
- Seventh Sprint/Version:
- Check security in/within code
- Eight Sprint/Version:
- Implement CRUD operation in local JSON or create mySQL DB o similar
- Nineth Sprint/Version:
- Go to web (
Spring Boot&React) - Go to desktop Java FX
- Go to web (
- Tenth Sprint/Version:
- Create extensions and publish
6 Try/Catch for wrong inputs
When executing Java code, different errors may occur: coding errors made by the programmer, errors due to wrong input, or other unforeseeable things.
When an error occurs, Java will normally stop and generate an error message. The technical term for this is: Java will throw an exception (throw an error).
The try and catch keywords come in pairs:
- The
trystatement allows you to define a block of code to be tested for errors while it is being executed. - The
catchstatement allows you to define a block of code to be executed, if an error occurs in the try block.
6.1 Example
The finally statement lets you execute code, aftertry...catch, regardless of the result
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hi");
try {
int[] myNumbers = {1, 2, 3};
// this code will crash: there is NO positin 10 in this array myNumbers
System.out.println(myNumbers[10]);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Something went wrong.");
} finally {
System.out.println("The 'try catch' is finished.");
}
System.out.println("Bye");
}
}
// Output:
// Hi
// Something went wrong.
// The 'try catch' is finished.
// Bye