React JS: useEffect
ReactJS hooks
📘 useEfect
useEffect allows you to perform side effects in your components. Some examples of side effects are: fetching data, directly updating the DOM, and timers.
useEffect lets you synchronize a component with an external system.
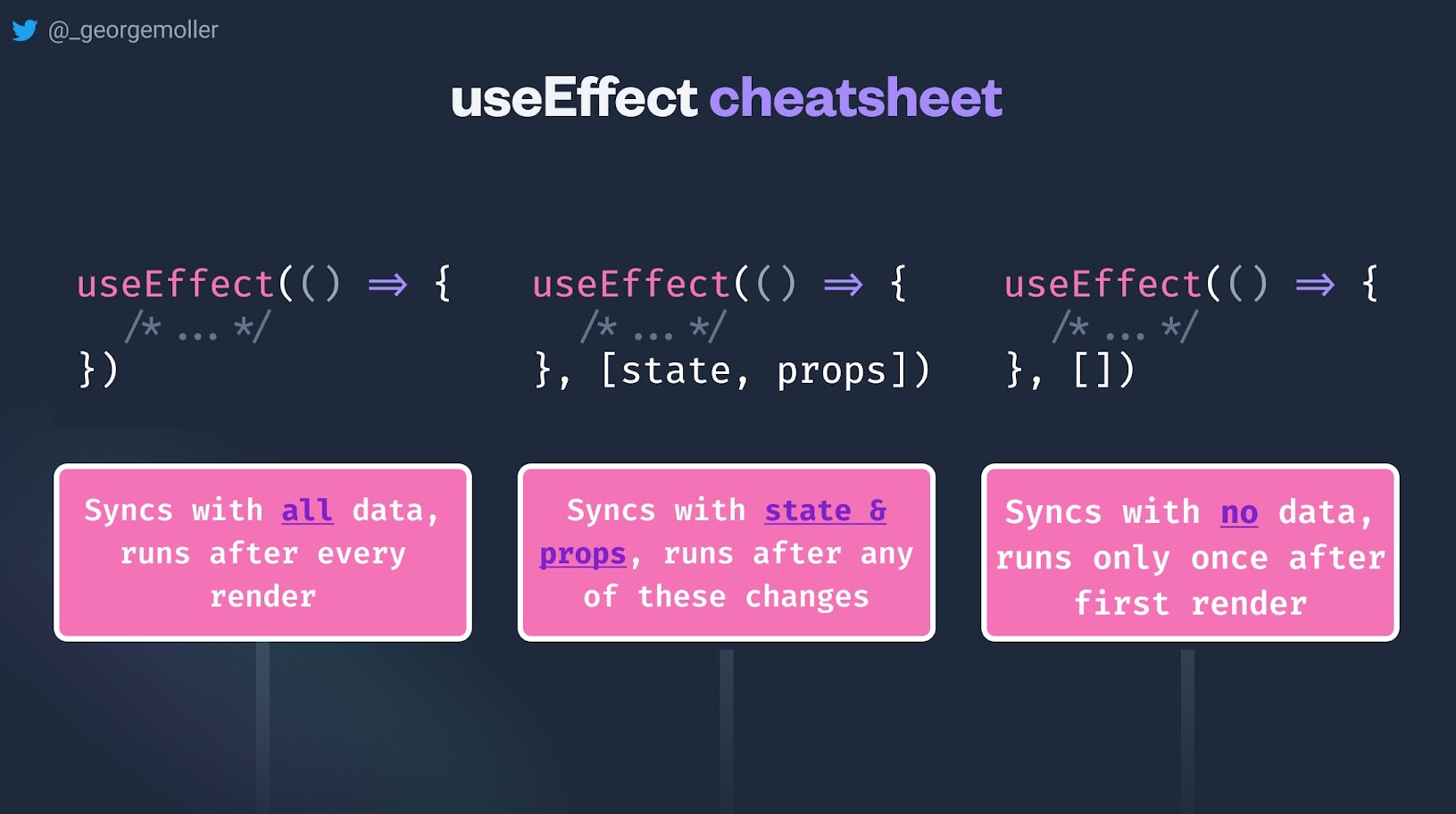
useEffect(setup, dependencies?)
1 Introduction
useEffect accepts two arguments. The second argument is optional.
“The question is not ‘when does this effect run,’ the question is ‘with which state does this effect synchronize?’” – Ryan Florence
useEffect(setup, dependencies?)
App.js
import { useEffect } from 'react';
import { createConnection } from './chat.js';
function ChatRoom({ roomId }) {
const [serverUrl, setServerUrl] = useState('https://localhost:1234');
useEffect(() => {
const connection = createConnection(serverUrl, roomId);
connection.connect();
return () => {
connection.disconnect();
};
}, [serverUrl, roomId]);
// ...
}useEffect is a Hook, so you can only call it at the top level of your component or your own Hooks. You can’t call it inside loops or conditions. If you need that, extract a new component and move the state into it.
If you’re not trying to synchronize with some external system, you probably don’t need an Effect.
1.1 Parameters
setup: The function with your Effect’s logic.- Your setup function may also optionally return a cleanup function.
- When your component is first added to the DOM, React will run your setup function.
- After every re-render with changed dependencies, React will first run the cleanup function (if you provided it) with the old values, and then run your setup function with the new values.
- After your component is removed from the DOM, React will run your cleanup function one last time.
optional dependencies: The list of all reactive values referenced inside of the setup code.- Reactive values include** props, state, and all the variables and functions declared directly inside your component bod**y.
When Strict Mode is on, React will run one extra development-only setup+cleanup cycle before the first real setup.
If some of your dependencies are objects or functions defined inside the component, there is a risk that they will cause the Effect to re-run more often than needed.
If your Effect wasn’t caused by an interaction (like a click), React will let the browser paint the updated screen first before running your Effect.
If your Effect is doing something visual (for example, positioning a tooltip), and the delay is noticeable (for example, it flickers), replace useEffect with useLayoutEffect.
Even if your Effect was caused by an interaction (like a click), the browser may repaint the screen before processing the state updates inside your Effect.
Effects only run on the client. They don’t run during server rendering.
1.2 Returns
useEffectreturns undefined.
Dependency array passed to useEffect:
- It’s optional. If you don’t specify it, the effect runs after each render.
- If it’s empty
([]), the effect runs once, after the initial render. - It must — or as we’ll see later, should — contain the list of values used in the effect. The effect runs after any of these values changes (and after the initial render).
- The array of dependencies is not passed as argument to the effect function.
2 Synchronizing with Effects
“The question is not ‘when does this effect run,’ the question is ‘with which state does this effect synchronize?’”
– Ryan Florence
Effects let you run some code after rendering so that you can synchronize your component with some system outside of React.
2.1 Effects & events
An event is an action triggered by the user or the system, while an effect is a consequence of an event, usually referring to a change or action that results from it.
What are the effects, really? Examples are:
- Fetching data
- Reading from local storage
- Registering and deregistering event listeners
- Upadating the DOM
- Timers
- Updating the document title
- Updating a state variable based on props change
- Cleanup operations
- Triggering animations or transitions
- Logging or analytics tracking
- Managing scroll position
React’s effects are a completely different animal than the lifecycle methods of class-based components.
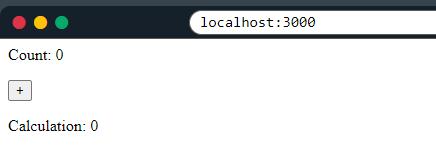
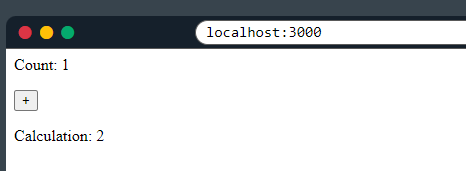
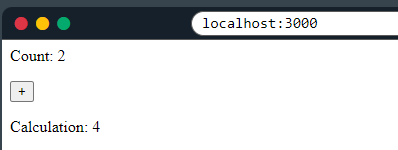
3 Example#1
In this example, the useEffect hook manages a state object with one field: count and a function-setter setCalculation.
App.js
import { useState, useEffect } from "react";
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const [calculation, setCalculation] = useState(0);
useEffect(() => {
setCalculation(() => count * 2);
}, [count]); // <- add the count variable here
return (
<>
<p>Count: {count}</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount((c) => c + 1)}>+</button>
<p>Calculation: {calculation}</p>
</>
);
}4 Example#2
By default useEffect will trigger anytime an update happens to the component.
This means if the component receives new props from its parent component or even when you change the state locally, the effect will run again.
If you don’t control the render cycle, you could run into an infinite loop of updates.
5 Example#3
This includes data fetching. When dealing with API calls using Axios, it’s essential to handle cleanup to prevent memory leaks and unexpected behavior. Below is a clear function demonstrating how to cancel an Axios API call using the useEffect hook:
DataSimulation.js
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import axios from 'axios';
const DataSimulation = () => {
const [data, setData] = useState(null);
const [error, setError] = useState(null);
useEffect(() => {
const source = axios.CancelToken.source();
const fetchData = async () => {
try {
const response = await axios.get('https://api.example.com/data', {
cancelToken: source.token,
});
setData(response.data);
} catch (error) {
if (axios.isCancel(error)) {
console.log('Request canceled:', error.message);
} else {
setError(error);
}
}
};
fetchData();
return () => {
source.cancel('Component unmounted - Cancelling API request');
};
}, []); // Empty dependency array means this effect will only run once
return (
<div>
{data && <p>Data: {data}</p>}
{error && <p>Error: {error.message}</p>}
</div>
);
};
export default DataSimulation;In this example:
- We import
useStateanduseEffectfrom React, andAxiosfor making API requests. - Inside the component, we define state variables data and error to manage API response and errors.
- In the
useEffecthook, we create an Axios cancel token usingCancelToken.source(). - We define an asynchronous function
fetchDatato make the API request usingAxiosand handle success/error cases. - The cleanup function returned from the
useEffectcancels the API request when the component unload. - The
useEffecthook is called once when the component loads ([] as dependency array).