Lab#SB00-4: API Rest
Spring Boot Library Management API Rest
📘 Spring Boot Lab#SB00-4: API Rest
After Lab#SB00-3 we are going to creata an API Rest just for book domain.
You may also check this introduction to API Rest.
1 Overview
An API is a set of definitions and protocols for building and integrating application software.
It’s sometimes referred to as a contract between an information provider and an information user—establishing the content required from the consumer (the
call) and the content required by the producer (theresponse).
For example, the API design for a weather service could specify that the user supply a zip code and that the producer reply with a 2-part answer, the first being the high temperature, and the second being the low temperature.
REST is a set of architectural constraints, not a protocol or a standard. API developers can implement REST in a variety of ways.
When a client request is made via a RESTful API, it transfers a representation of the state of the resource to the requester or endpoint.
This information, or representation, is delivered in one of several formats via HTTP: JSON (Javascript Object Notation), HTML, XLT, Python, PHP, or plain text.
JSON is the most generally popular file format to use because, despite its name, it’s language-agnostic, as well as readable by both humans and machines.
2 HTTP messages
HTTP messages are how data is exchanged between a server and a client.
There are two types of messages:
requestssent by the client to trigger an action on the server,- and
responses, the answer from the server.
HTTP messages are composed of textual information encoded in ASCII, and span over multiple lines.
In HTTP/1.1, and earlier versions of the protocol, these messages were openly sent across the connection. In HTTP/2, the once human-readable message is now divided up into HTTP frames, providing optimization and performance improvements.
HTTP requests, and responses, share similar structure and are composed of:
- A start-line describing the requests to be implemented, or its status of whether successful or a failure. This start-line is always a single line.
- An optional set of HTTP headers specifying the request, or describing the body included in the message.
- A blank line indicating all meta-information for the request has been sent.
- An optional body containing data associated with the request (like content of an HTML form), or the document associated with a response. The presence of the body and its size is specified by the start-line and HTTP headers.
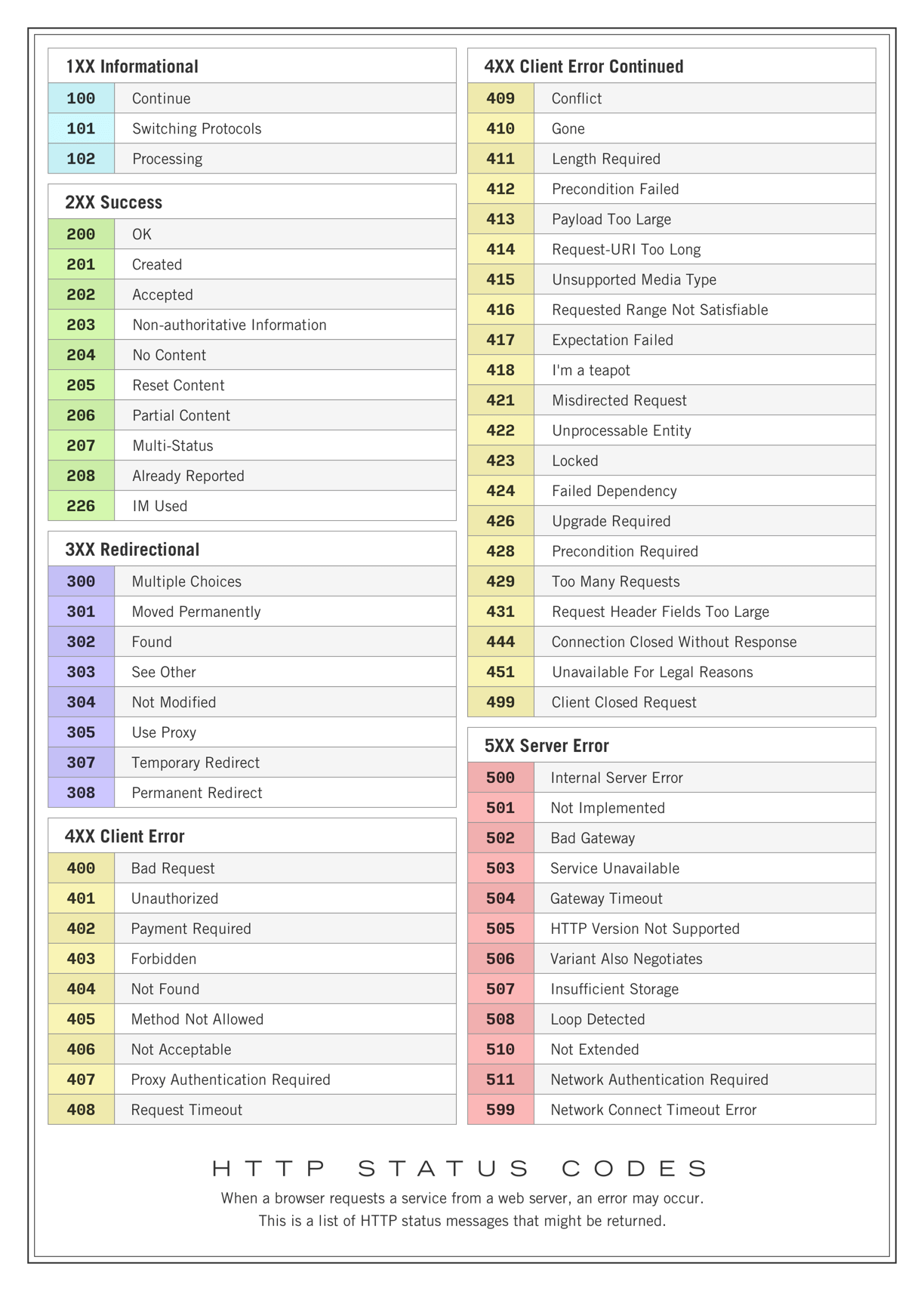
3 HTTP status messages
4 Library Management base project
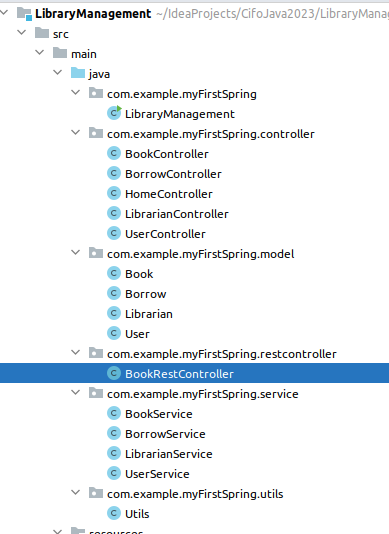
5 Folder-tree project
6 API Rest book
Reference:
This annotation is used at the class level and allows the class to handle the requests made by the client. The RestController allows to handle all REST APIs such as GET, POST, Delete, and PUT requests.
We define a REST controller using the @RestController and @RequestMappingannotations. The controller handles requests related to books under the base path "/api/book".
The BookRestController class has a dependency on the BookService class, which is automatically injected using the @Autowired annotation.
The controller has a GET method mapped to the "/books" path, which retrieves all the books using the bookService.getAllBooks() method and returns them as a HashMap with String keys and Book values.
This method can be accessed through a web browser or another client, and it will return the response in a format such as JSON or XML.
package com.example.myFirstSpring.restcontroller;
import com.example.myFirstSpring.model.Book;
import com.example.myFirstSpring.service.BookService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.HashMap;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/book")
public class BookRestController {
@Autowired
BookService bookService;
@GetMapping ("/books")
public HashMap<String, Book> getAllBooks(){
return bookService.getAllBooks();
}
}7 Postman
Postman is a popular API development tool used by developers to test, design, and document APIs.
With Postman, developers can send requests to APIs and receive responses, allowing them to check the functionality of the API and identify any issues that need to be fixed.
Postman also allows developers to create collections of requests and to collaborate with other developers by sharing these collections.
7.1 Install Postman in Linux Mint
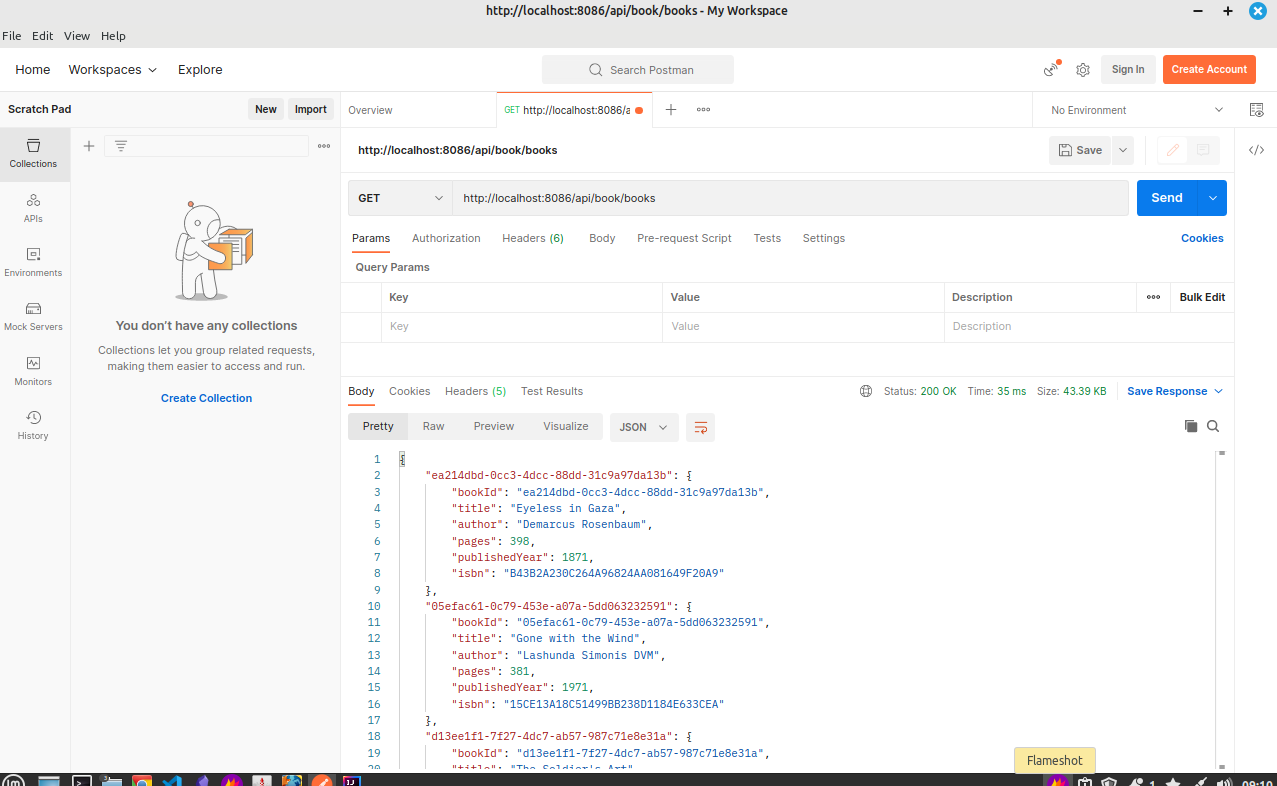
endpoint: http://localhost:8086/api/book/books
7.2 Using variables
Variables enable you to store and reuse values in Postman.
By storing a value as a variable, you can reference it throughout your collections, environments, requests, and test scripts. Variables help you work efficiently, collaborate with teammates, and set up dynamic workflows.
8 Swagger
Swagger, on the other hand, is an open-source framework for designing and documenting APIs.
With Swagger, developers can create an API specification that defines the endpoints, parameters, and responses of an API.
This specification can then be used to generate documentation, client libraries, and server stubs in multiple programming languages.
Swagger also includes a user interface called Swagger UI, which allows developers to interact with an API and explore its endpoints and responses.
8.1 Add Swagger to Spring
Add Swagger to project, swagger web and refactor:
http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
- Java Version and dependencies
Dependencies:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger2 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger-ui -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>- Annotation:
@EnableSwagger2 in Main
- application.properties:
spring.mvc.pathmatch.matching-strategy=ant-path-matcher
- java class config:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@EnableSwagger2
@Configuration
public class SpringFoxConfig {
@Bean
public Docket api() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors
.any())
.paths(PathSelectors
.any())
.build();
}
}9 Versions
endpoint: http://localhost:8090/api/book/books
| Code Version | Commit | Folder-Tree | Screeshoots |
|---|---|---|---|
| Library Management Rest 0.0 | create project pom and refactoring, CRUD: read all books | Basic Structure | localhost:8090/api/book/books |
| Library Management Rest 0.1 | CRUD: delete book | - | localhost:8090/api/book/deleteBook |
| Library Management Rest 0.2 | CRUD: create book & create borrow by ids | - | localhost:8090/api/book/books - localhost:8090/api/user/users - localhost:8090/api/borrow/createBorrow |
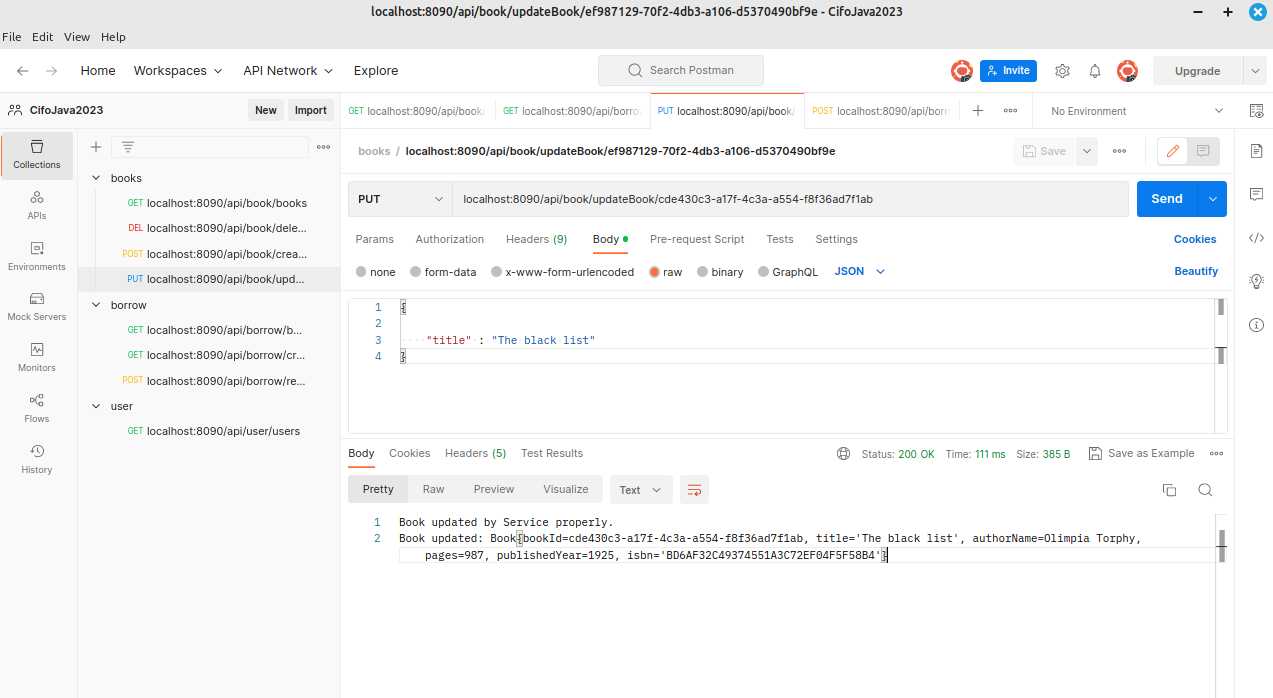
| Library Management Rest 0.3 | CRUD: update book and update method in book model | Final structure | localhost:8090/api/book/updateBook |
| Library Management Rest 0.4 | user CRUD |
9.1 Postman apis
| Domain | Link | Objects |
|---|---|---|
| books | postman link | book |
| borrow | postman link | book user borrow |
| user | postman link | user |