React JS App: async
ReactJS async
1 Overview
📘 async
Async/await is a syntax in JavaScript that makes it easier to work with asynchronous code and allows you to write it easier, read and understand, by making it look more like synchronous code.
Asynchronous programming is a technique that enables your program to start a potentially long-running task and still be able to be responsive to other events while that task runs, rather than having to wait until that task has finished.
Once that task has finished, your program is presented with the result.
Many functions provided by browsers, especially the most interesting ones, can potentially take a long time, and therefore, are asynchronous. For example:
- Making
HTTPrequests using fetch() - Accessing a user’s camera or microphone using getUserMedia()
- Asking a user to select files using showOpenFilePicker()
2 Synchronous programming
Synchronous code is code that is executed in a “synchronous” manner, meaning that it is executed in the order that it appears in the source code. When a line of synchronous code is executed, the program will wait for it to complete before moving on to the next line of code.
In this example, the code will execute the console.log('Start') line first, then wait for the doSomething() function to complete and return a result, and then log the result to the console. Finally, it will execute the console.log('End') line.
Synchronous code is easy to understand and debug, because the order of execution is clear and predictable. However, it can be less efficient than asynchronous code, because it can block the program from moving on to other tasks until the current task is complete.
Synchronouscode may be is easy but blocking.
This is the basic problem with long-running synchronous functions. What we need is a way for our program to:
- Start a long-running operation by calling a function.
- Have that function start the operation and return immediately, so that our program can still be responsive to other events.
- Notify us with the result of the operation when it eventually completes.
That’s precisely what asynchronous functions can do.
Best with async/await but promises must be studied
3 Asynchronous programming
Asynchronous programming is a programming paradigm that enables the execution of tasks independently, without waiting for previous tasks to complete.
It allows programs to handle multiple operations concurrently, enhancing efficiency and responsiveness.
In asynchronous programming, tasks are initiated and then executed in the background, allowing the program to continue its execution without being blocked by long-running operations.
Non-blocking refers to the characteristic of a program or system that doesn’t halt or get stuck waiting for a resource or operation.
In the context of asynchronous programming, non-blocking refers:
- to the ability of a task or operation to proceed independently without blocking other tasks from executing.
- It ensures that tasks can run concurrently without causing delays, allowing for efficient utilization of system resources and improved overall performance.
- Non-blocking operations are often used in conjunction with asynchronous programming to achieve scalability and responsiveness in applications.
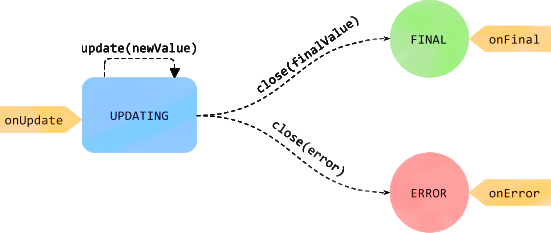
3.1 async function
The async and await keywords enable asynchronous, promise-based behavior to be written in a cleaner style, avoiding the need to explicitly configure promise chains.
The async function declaration declares an
asyncfunction where theawaitkeyword is used within the function body.
App.js
In this example, the greet function is an async function that returns a promise that resolves to the string “Hello, world!”. The main function is also an async function that calls the greet function and waits for the promise to resolve using the await keyword. When the promise resolves, the value is assigned to the message variable and logged to the console.
Async functions can contain zero or more await expressions. Await expressions make promise-returning functions behave as though they’re synchronous by suspending execution until the returned promise is fulfilled or rejected.
The resolved value of the promise is treated as the return value of the await expression. Use of async and await enables the use of ordinary try / catch blocks around asynchronous code.
4 Example 1:marketplace
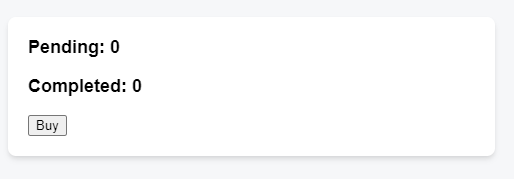
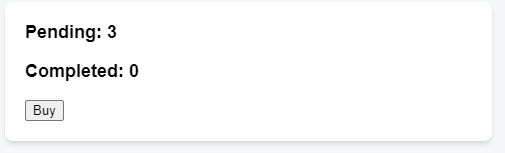
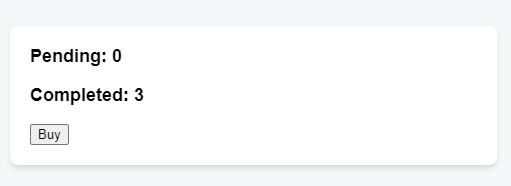
You’re working on an art marketplace app that lets the user submit multiple orders for an art item at the same time.
Each time the user presses the “Buy” button, the “Pending” counter should increase by one. After three seconds, the “Pending” counter should decrease, and the “Completed” counter should increase.
App.js
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function RequestTracker() {
const [pending, setPending] = useState(0);
const [completed, setCompleted] = useState(0);
async function handleClick() {
setPending(p => p + 1);
await delay(3000);
setPending(p => p - 1);
setCompleted(c => c + 1);
}
return (
<>
<h3>
Pending: {pending}
</h3>
<h3>
Completed: {completed}
</h3>
<button onClick={handleClick}>
Buy
</button>
</>
);
}
function delay(ms) {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(resolve, ms);
});
}