Team & the Specialist
SCRUM Step 8
📘 Summary: SCRUM Step 8 - Team & the specialist
In SCRUM, the Development Team plays a pivotal role in delivering a potentially releasable product increment at the end of each Sprint.
The team’s self-organizing and cross-functional nature, combined with the absence of formal titles or sub-teams, ensures collective accountability.
However, recognizing individual members’ specialized skills is crucial, even if it does not belong to formal SCRUM.
The introduction of specialists can significantly contribute to a project’s success by providing deep expertise in specific domains.
While deviations from standard roles are permissible, adherence to SCRUM principles remains essential. Specialists, such as Security Analysts, Data Scientists, UX/UI Designers, and others, bring valuable expertise for solving complex problems within their domains. The SCRUM guide emphasizes maintaining the essence of SCRUM while accommodating organizational needs, making it vital to clearly define a specialist’s role, responsibilities, and interactions within the SCRUM framework for effective implementation.
Keywords: SCRUM Step 8 - Team & the specialist
Team & the Specialist, Development Team, Self-organizing, Cross-functional, Formal Titles, Deep Expertise, Accountability, Essence of SCRUM, Organizational Needs, Roles and Responsibilities, Problem Solving.
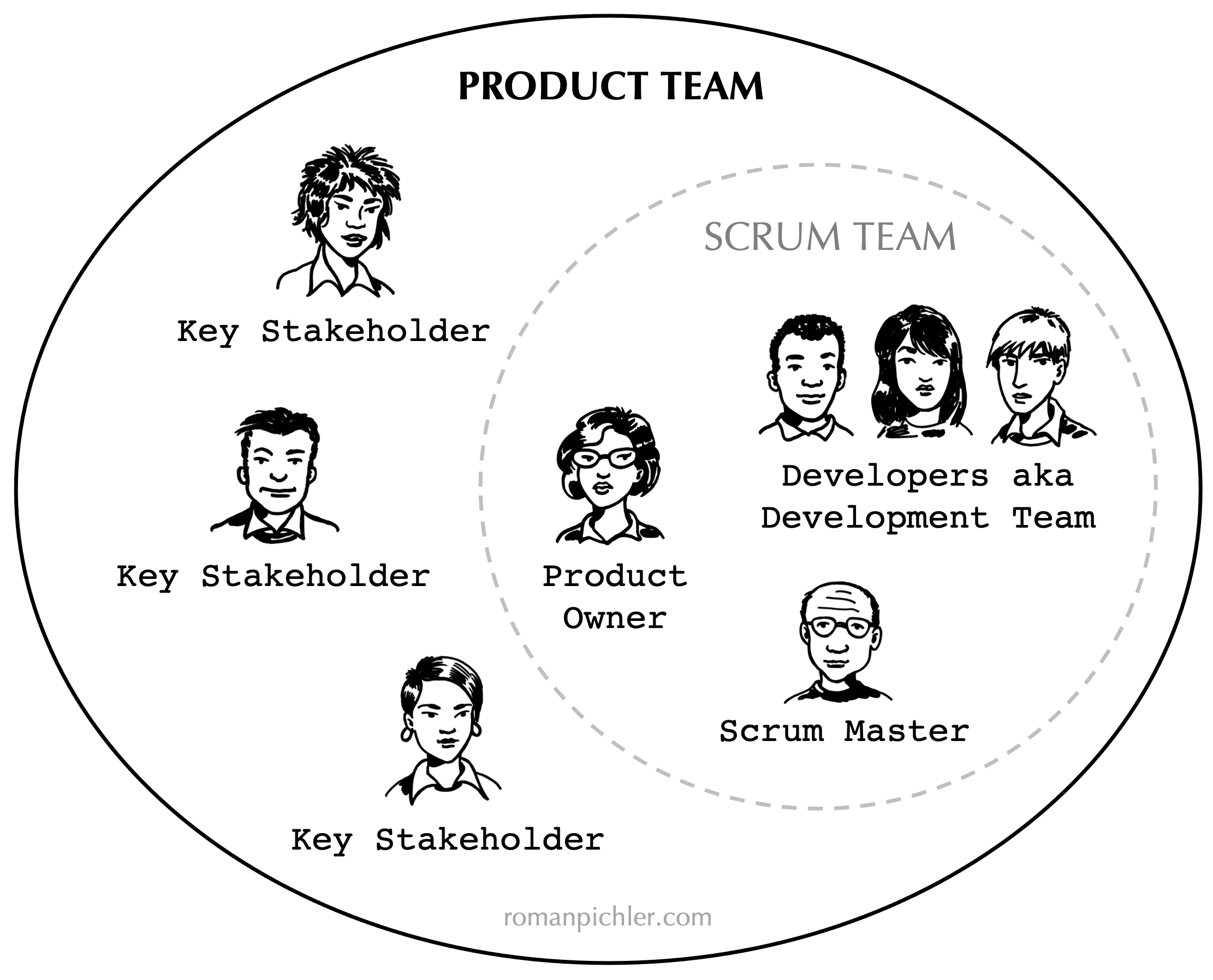
1 First at all, the Team
According to the Scrum Guide, the Development Team “consists of professionals who do the work of delivering a potentially releasable Increment of “Done” product at the end of each Sprint.
Only members of the Development Team create the Increment. Development Teams are structured by the organization to organize and manage their own work.”
Development Teams are hence essential to Scrum’s built-in checks & balances as the Development Team has the sole control over the Sprint Backlog and is watching over the Definition of “Done”.
Generally, Development Teams need to have the following characteristics to be successful:
- They are self-organizing. No one (not even the Scrum Master) tells the Development Team how to turn Product Backlog into Increments of potentially releasable functionality;
- Development Teams are cross-functional, with all the skills as a team necessary to create a product Increment;
- Scrum recognizes no titles for Development Team members, regardless of the work being performed by the person;
- Scrum recognizes no sub-teams in the Development Team, regardless of domains that need to be addressed like testing, architecture, operations, or business analysis; and,
- Individual Development Team members may have specialized skills and areas of focus, but accountability belongs to the Development Team as a whole.
2 The specialist role
The role of a specialist in a team can be crucial for the success of a project. Specialists bring deep expertise in a specific area, and their contributions can enhance the overall quality and efficiency of the team’s work.
While the traditional roles are well-established in Scrum (Scrum Master, Team, Product Owner), some companies may introduce additional roles based on their specific needs or organizational structure.
It’s important to note that while deviations from the standard roles might work for some organizations, it’s crucial to ensure that the essence and principles of Scrum are maintained for the effective implementation of agile practices.
If a “specialist” role is introduced, it’s essential to clarify its responsibilities, interactions with other roles, and how it contributes to the overall success of the Scrum team.
Here are a few aspects of a specialist’s role in a team:
- Expertise: Specialists typically have a high level of expertise in a specific domain, whether it’s in technology, design, operations, or another field. This expertise is valuable for solving complex problems and making informed decisions within their domain.
- Problem Solving: Specialists are often called upon to solve intricate problems that require their specific knowledge and skills. Their ability to analyze and address challenges in their area of expertise can be critical for the team’s success.
2.1 Specialist examples
- Security Analyst in Cybersecurity:
- Role: Analyzing and enhancing the security infrastructure of a software product.
- Expertise: Deep knowledge of security vulnerabilities, threat modeling, and best practices for secure coding.
- Data Scientist in Analytics:
- Role: Extracting meaningful insights from data to inform business decisions.
- Expertise: Statistical analysis, machine learning, and data visualization techniques.
- UX/UI Designer in User Experience:
- Role: Crafting the user interface and overall user experience of a digital product.
- Expertise: Information architecture, usability principles, and design thinking.
- DevOps Engineer in Operations:
- Role: Streamlining the development-to-operations pipeline for faster and more reliable software delivery.
- Expertise: Automation, continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD), and infrastructure as code.
- Network Architect in Networking:
- Role: Designing and implementing the organization’s network infrastructure.
- Expertise: Routing and switching protocols, network security, and scalability.
- Machine Learning Engineer in Artificial Intelligence:
- Role: Developing and deploying machine learning models for predictive analytics.
- Expertise: Algorithms, model training, and evaluation, deep learning frameworks.
- Forensic Accountant in Finance:
- Role: Investigating financial discrepancies and providing expert testimony in legal cases.
- Expertise: Accounting principles, fraud detection, and financial analysis.
- Clinical Researcher in Healthcare:
- Role: Conducting and overseeing clinical trials to advance medical research.
- Expertise: Regulatory compliance, patient safety, and data integrity in clinical studies.
- SEO Specialist in Digital Marketing:
- Role: Optimizing online content to improve search engine rankings.
- Expertise: Keyword analysis, on-page optimization, and staying current with search engine algorithms.
- Hardware Engineer in Electronics:
- Role: Designing and developing electronic components and systems.
- Expertise: Circuit design, PCB layout, and knowledge of electronic components.