classDiagram
direction LR
class Person {
-name: String
}
class Passport {
-passportNumber: String
}
Person "1" *-- "1" Passport: Owns
Java Patterns: UML
Java Fundamentals and Patterns
1 Definition
UML stands for Unified Modeling Language. It is a standardized visual language for specifying, constructing, visualizing, and documenting the artifacts of software systems, as well as for business modeling and other non-software systems.
UML is used by software developers, business analysts, and systems engineers to model the design of a system and communicate that design to others. It provides a common language that allows people from different disciplines to understand and discuss system design in a consistent and precise way.
UML is a powerful tool that can help teams design and develop software and other systems more efficiently and effectively.
2 Class diagram and relationships
In UML, there are several types of relationships that can be used to model the relationships between elements in a system. Here is a brief overview of some of the most common types of relationships:
- Inheritance: Inheritance is a relationship between classes, where one class is a subclass of another class and inherits the properties and behavior of the superclass. This is represented in UML by a solid line with a closed, filled arrowhead pointing from the subclass to the superclass.
- Composition: Composition is a strong type of association that represents a whole-part relationship between two classes, where the parts cannot exist independently of the whole. This is represented in UML by a solid line with a closed diamond shape pointing from the whole to the part.
- Aggregation: Aggregation is a weaker type of association that represents a whole-part relationship between two classes, where the parts can exist independently of the whole. This is represented in UML by a solid line with an open diamond shape pointing from the whole to the part.
- Association: Association is a relationship between two classes that represents a connection or relationship between them. This is represented in UML by a solid line with an open arrowhead pointing from one class to the other.
- Dependency: Dependency is a relationship between two classes that indicates that one class depends on the other for its functionality. This is represented in UML by a dashed line with an open arrowhead pointing from the dependent class to the class it depends on.
- Use: Use is a relationship between two classes that indicates that one class uses the other in some way. This is represented in UML by a dashed line with an open, unfilled arrowhead pointing from the using class to the class being used.
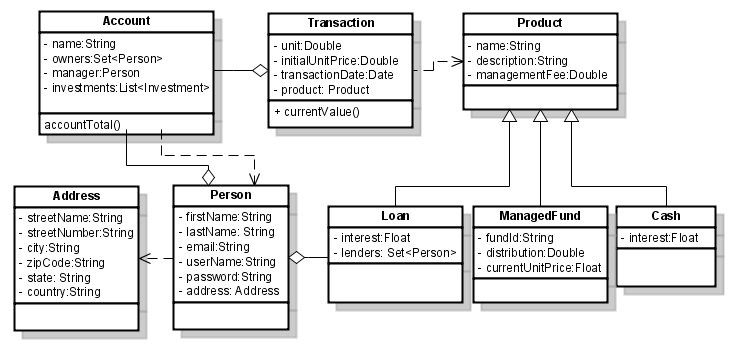
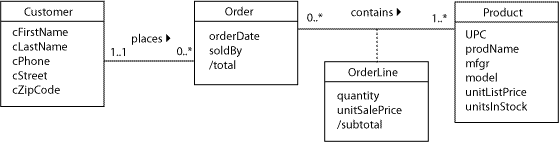
3 Example: class and object diagram
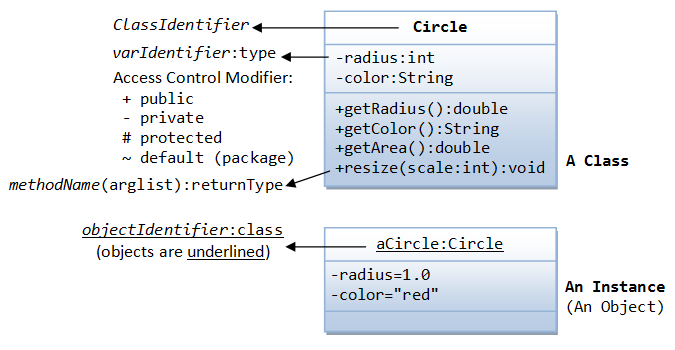 `
`
4 Entity relationship types: multiplicity
4.1 One-to-One (1:1)
A one-to-one relationship is a relationship between two entities where one entity is related to exactly one instance of the other entity.
For example, a person can have only one passport, and a passport can belong to only one person. In this case, the person entity and the passport entity have a one-to-one relationship.
4.2 One-to-Many (1:n)
A one-to-many relationship is a relationship between two entities where one entity is related to many instances of the other entity.
classDiagram
direction LR
class Author {
-name: String
}
class Book {
-title: String
}
Author "1" *-- "*" Book: Writes
For example, one author can write many books, and a book can have only one author. In this case, the author entity and the book entity have a one-to-many relationship.
4.3 Many-to-Many (n:m)
A many-to-many relationship is a relationship between two entities where many instances of one entity are related to many instances of the other entity.
classDiagram
direction LR
class Student {
-name: String
}
class Course {
-title: String
}
Student "*" *--* "*" Course: Enrolls
For example, many students can be enrolled in many courses, and many courses can have many students. In this case, the student entity and the course entity have a many-to-many relationship.
5 Example: Customer-Product
5.1 Customer-Product relationship
The model of the relationships between Customer, Order and Product is not enough.
classDiagram
direction LR
class Customer {
-name: String
}
class Order {
-idOrder: String
}
class Product {
-productName: String
}
Customer "1" *-- "*" Order: Places
Order "*" *--* "*" Product: Contains
5.2 Defining the Customer-Product relationship
The model of the relationships between Customer, Order and OrderDetail and Product.
There is a one-to-many association between Customer and Order, but how should we represent Order / OrderDetail / Product? We have chosen to map OrderDetail as an association class representing the many-to-many association between Order and Product.
classDiagram
class Customer {
-name: String
}
class Order {
-idOrd: String
}
class OrderDetail {
-idOrdD: String
}
class Product {
-idPro: String
}
Customer "1" *-- "*" Order: Places
Order "1" *-- "*" OrderDetail: Contains
OrderDetail "*" --* "1" Product: Contains