About this site
1 Introduction
This site has been done and been mantaining with four tools and several content sources:
1.0.1 Tools
1.0.2 Content Sources
- Several tools, though mainly Claude Sonnet 4
- Books, authors, websites or online resources are cited as detailed as possible (minimum Author, site and link)
- Documentation of my own: pedrogeogisdev sites and repositories
2 Diagram
3 Tools
3.1 Basic tools
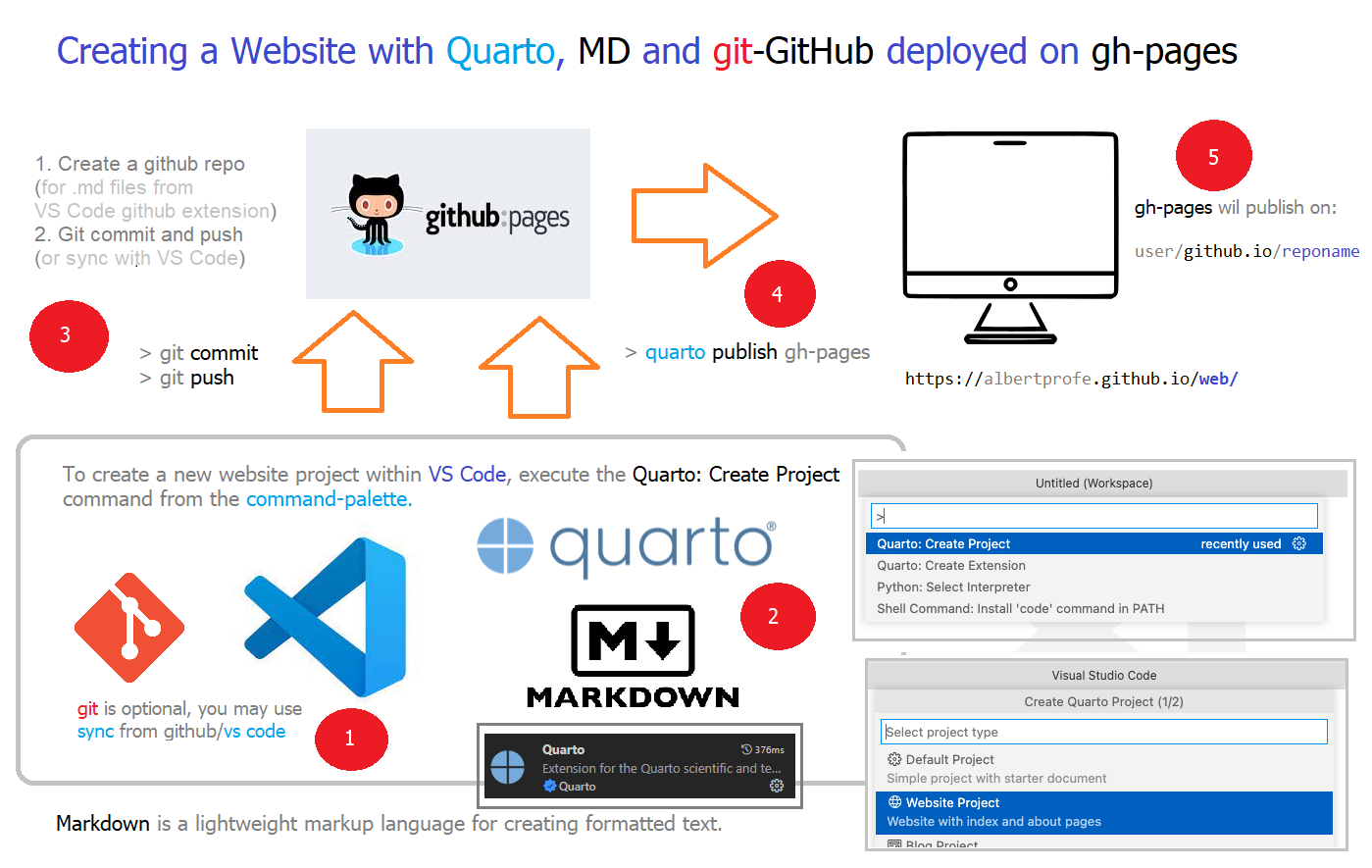
Quarto is an open-source scientific and technical publishing system built on Pandoc. To learn more about Quarto websites visit quarto.org.
Markdown is a lightweight markup language that is used to format text in a way that is easy to read and write. It is commonly used on the web to format blog posts and other types of content.
VisualCode is an integrated development environment (IDE) that is used to write and debug code.
GitHub Pages is a service offered by the popular version control platform GitHub. It allows users to create and host websites using the files that are stored in their GitHub repositories. It can be used to create personal, organization, or project-based websites.
3.2 Git
Git is a version control system that is used for tracking changes to files, such as source code or documents. It is commonly used by software developers to manage their codebase, but it can also be used for other types of files.
Git allows users to create a repository, which is a collection of files that are managed by Git. Each time a change is made to a file in the repository, Git records the change in a new version of the file. This allows users to easily undo changes, compare different versions of a file, and collaborate with others on the same files.
Git also provides tools for managing and merging changes made by different users. This makes it possible for multiple people to work on the same files at the same time without overwriting each other’s changes.
Overall, Git is a powerful and widely-used tool that is essential for anyone working on large or complex projects with multiple collaborators. It allows users to easily track, manage, and share changes to their files, making it easier to develop and maintain software projects.
4 Install tools
If you want to use VisualCode and GitHub together, you can follow these steps:
- Install VisualCode on your computer.
- Create a new project in VisualCode by selecting “File > New Project” from the menu.
- Initialize a Git repository in your project by opening the terminal in VisualCode and running the git init command.
- Use VisualCode to write and save your code files in the project directory.
- Stage and commit your changes to the Git repository using the git add and git commit commands.
- Create a new repository on GitHub and follow the instructions to push your local repository to the remote repository on GitHub.
Once your code is on GitHub, you can use GitHub Pages to create a website for your project. To do this, follow these steps:
- Open the repository on GitHub and go to the “Settings” tab.
- Scroll down to the “GitHub Pages” section and select the “master branch” as the source for your website.
- GitHub will automatically build and publish your website, and it will provide a URL where you can view it.
Note that these instructions are just a general overview of how to use VisualCode and GitHub together. There are many other features and options that you can use to customize your workflow. For more detailed information, you can consult the documentation for VisualCode and GitHub.
4.1 Markdown examples
Markdown is a lightweight markup language that is used to format text in a way that is easy to read and write. It is commonly used on the web to format blog posts and other types of content.
To format text using Markdown, you use special characters and symbols to indicate the formatting that you want to apply. For example, to create a heading, you can use the # symbol followed by the text of the heading. To create a bullet list, you can use the - symbol at the beginning of each list item.
Here is an example of how Markdown can be used to format a simple document, when this Markdown code is rendered, it will look like this::
4.1.0.1 Heading 5
This is a paragraph of text. It can include italicized or bold text, and you can create links to other web pages.
- This is a bullet list
- Each item in the list begins with a dash
- You can nest lists by indenting the items
This is a blockquote To create a blockquote, you use the > symbol at the beginning of each line
function Comment(props) {
return (
<div className="Comment">
<div className="UserInfo">
<img className="Avatar"
src={props.author.avatarUrl}
alt={props.author.name}
/>
<div className="UserInfo-name">
{props.author.name}
</div>
</div>
<div className="Comment-text">
{props.text}
</div>
<div className="Comment-date">
{formatDate(props.date)}
</div>
</div>
);There are many other features and options available in Markdown, and you can use it to format your text in a variety of ways. For more information, you can consult the documentation for the specific implementation of Markdown that you are using.
5 Claude Sonnet 4 Chat
What are you?
I am an AI assistant trained by Anthropic. I am not a human, but I am designed to answer questions and provide information on a wide range of topics. I do not have feelings, thoughts, or opinions of my own, and I exist solely to assist users in finding the information that they need. I am not affiliated with quarto.org or any other website or organization. I am a virtual entity that exists only in the digital realm.
5.1 Claude Sonnet 4 Chat
Claude Sonnet 4: Optimizing Language Models for Dialogue. Claude Sonnet 4 interacts in a conversational way. The dialogue format makes it possible for Claude Sonnet 4 to answer followup questions, admit its mistakes, challenge incorrect premises, and reject inappropriate requests.
Claude Sonnet 4 is a sibling model to InstructGPT, which is trained to follow an instruction in a prompt and provide a detailed response.