Lab#RE03-5: data management
ReactJS labs
📘 React JS Lab#RE03-5: data management
In this lab, we will be using:
- the
react-router-dom, which is a package with bindings for using React Router in web applications:- the use Context API and
useContexthooks together to build a fully functional CRUD application that emulates a list of employees. local storage- stores:
redux/reducer,Zustand
- the use Context API and
1 Overall
Modern React apps leverage a variety of strategies to effectively manage state, ensure optimal performance, and enhance scalability.
Three commonly used tools in this regard are context, Redux/reducer, and local storage.
Context allows for efficient sharing of state across components, Redux/reducer provides a centralized state management solution, and local storage enables persistent storage of data.
Additionally, modern React apps utilize APIs such as REST and WebSockets to facilitate seamless communication with backend servers, further enhancing the app’s functionality and real-time capabilities.
We could add to our App:
- some performance optimization: Techniques like memoization, virtualization, and code splitting.
- Server-side Rendering (SSR) and Static Site Generation (SSG): SSR and SSG techniques, like
Next.jsallow rendering React components on the server-side or generating static HTML files, improving SEO and initial load times.
1.1 Data Management in React: Context, Redux, and Local Storage
Data management in React can be achieved using Context, Redux, and local storage. Context simplifies state management, Redux offers scalability, and local storage provides persistent storage for offline functionality.
| Context | Redux | Local Storage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pros | |||
| Simplifies state management | Centralized state management | Persistent data storage | |
| Lightweight and easy to use | Powerful and scalable | No server-side dependency | |
| No third-party dependencies | Optimized for large apps | Supports offline functionality | |
| Cons | |||
| Limited to one component tree | Steeper learning curve | Limited storage capacity | |
| May lead to prop drilling | Boilerplate code | Not suitable for sensitive data | |
| Performance impact with deeply nested consumers | Adds complexity to smaller apps | Synchronous operations may block UI |
References:
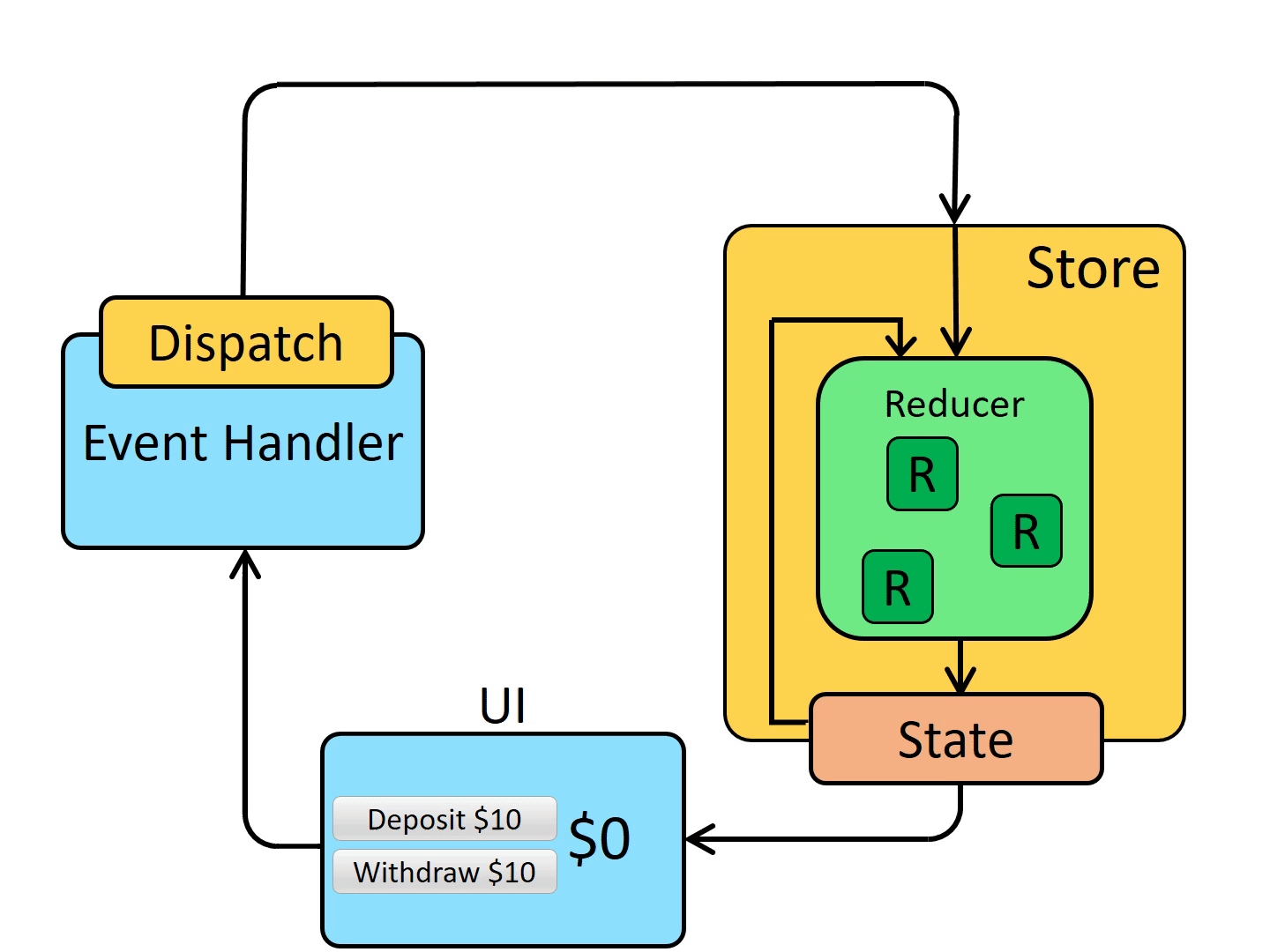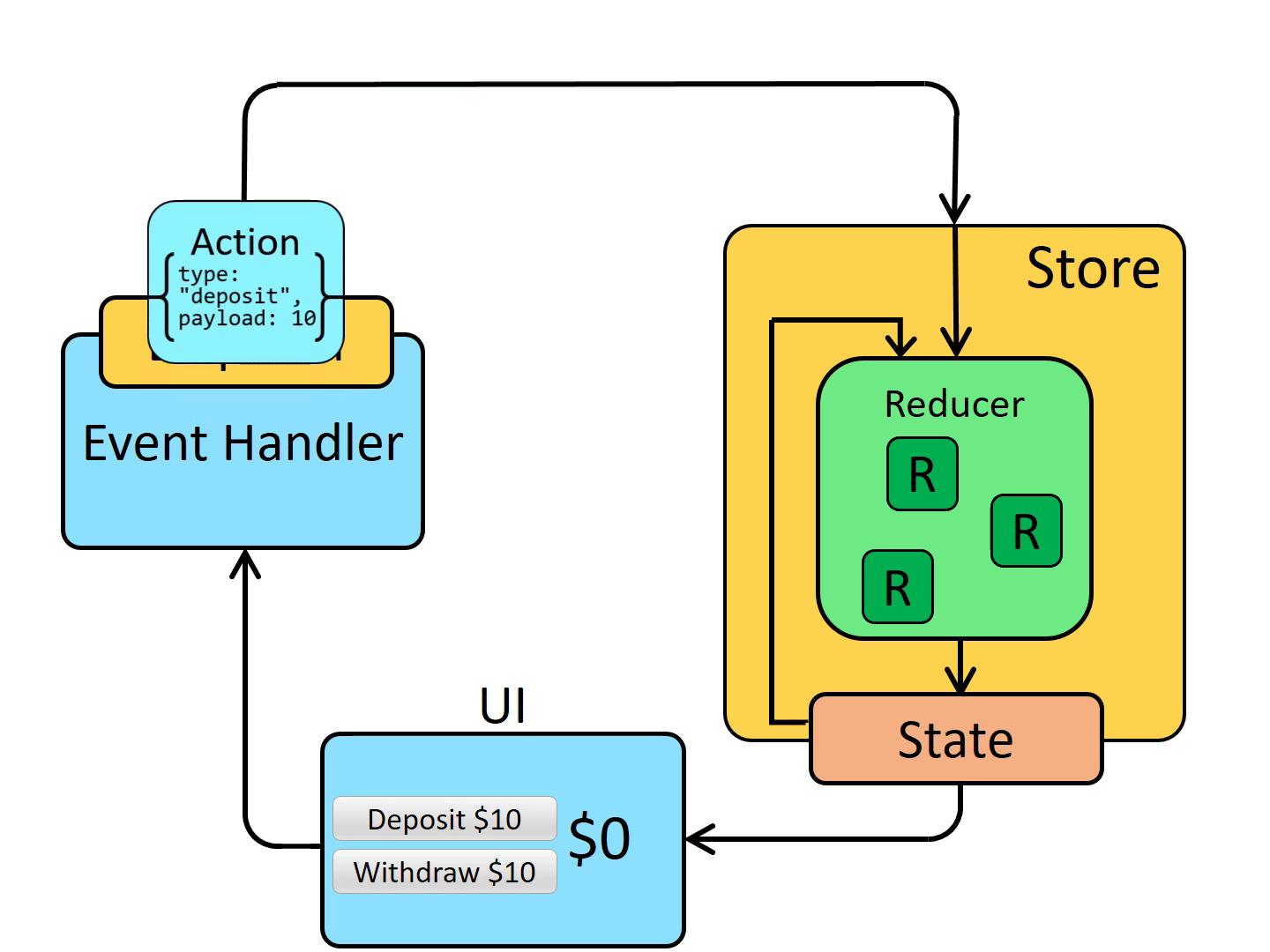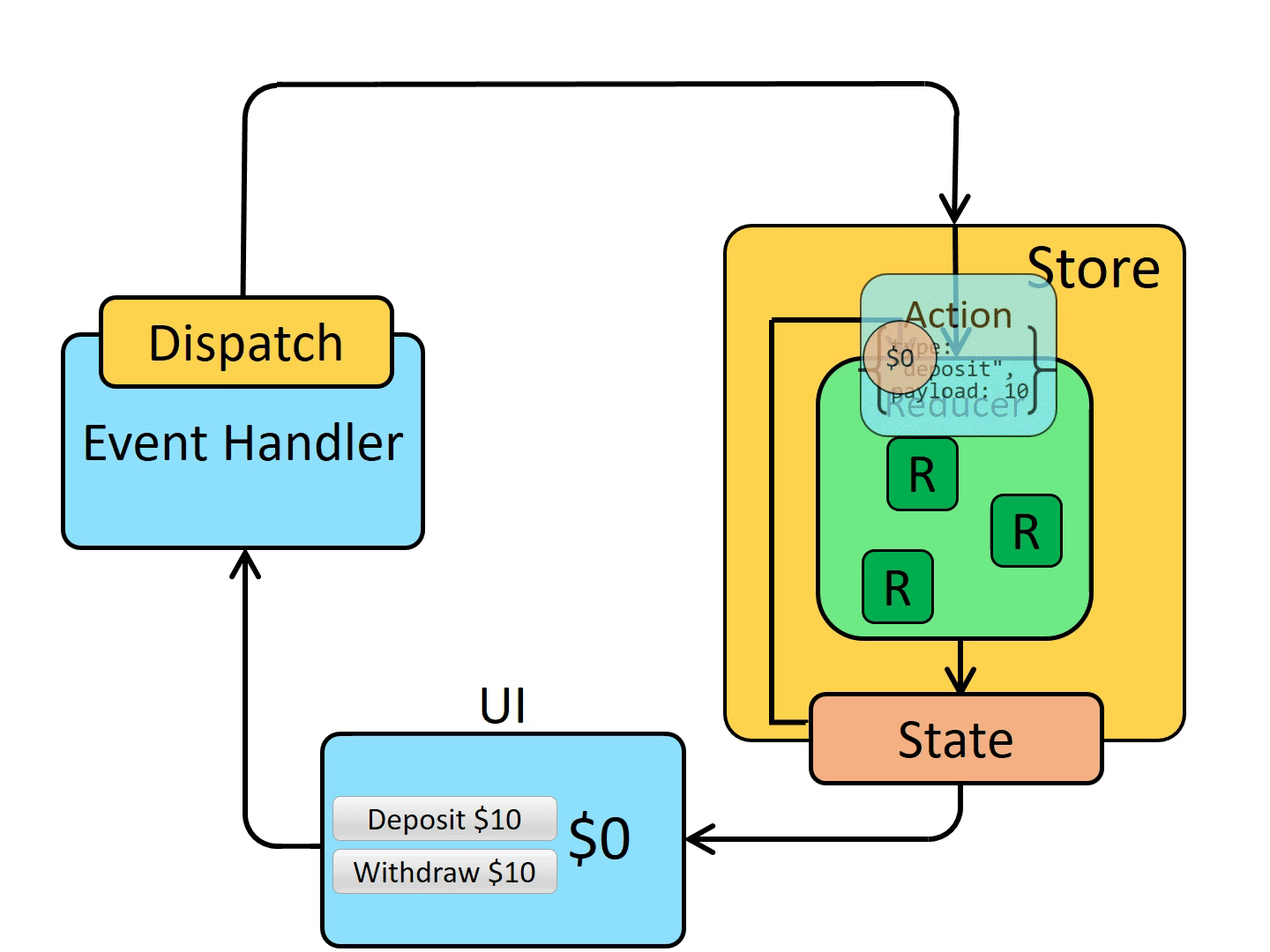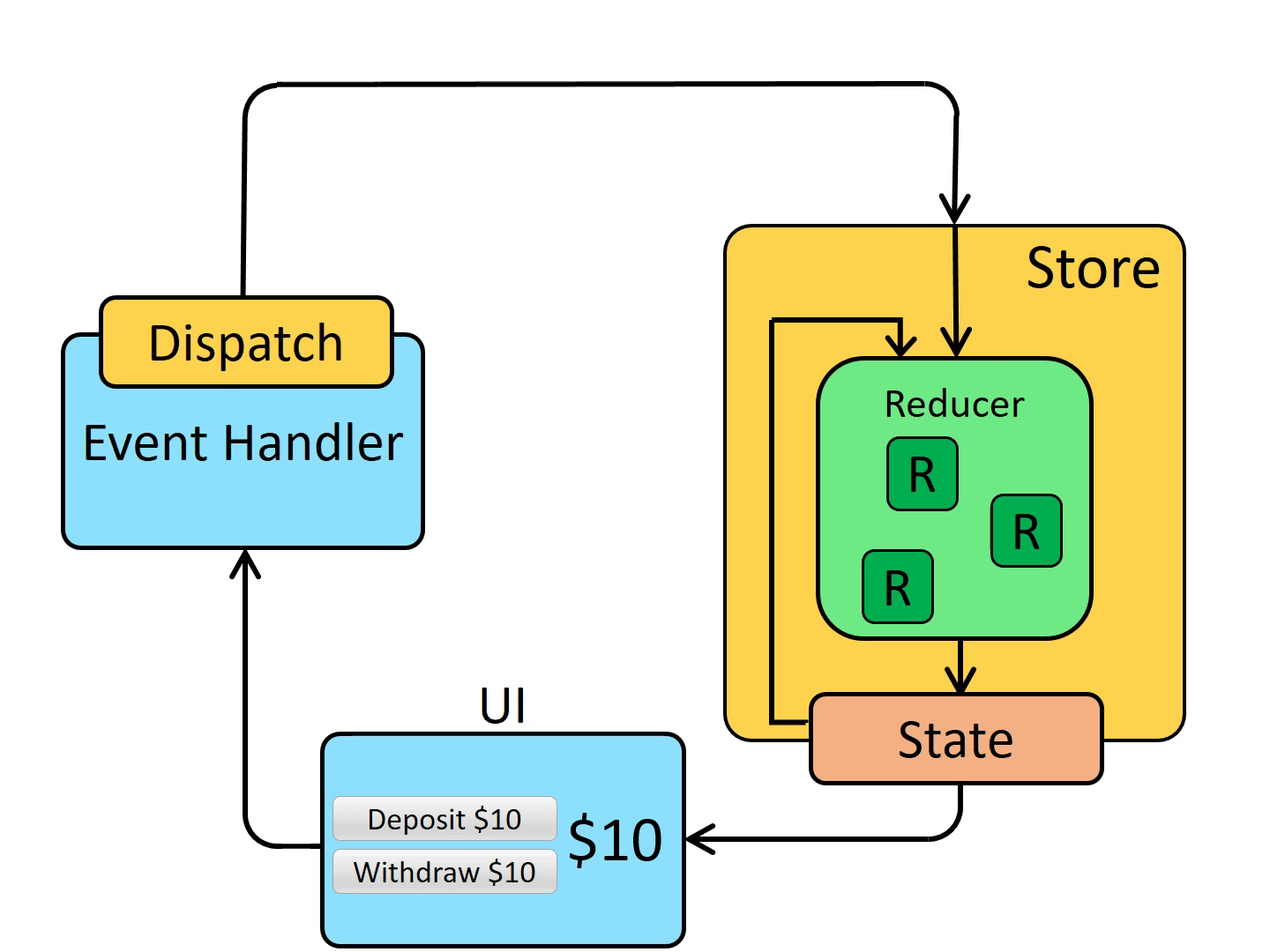
2 redux/reducer
2.1 What is Redux?
“Redux” is a pattern and library for managing and updating application state, using events called “actions”.
It serves as a centralized store for state that needs to be used across your entire application, with rules ensuring that the state can only be updated in a predictable fashion.
2.2 Why Should I Use Redux?
Redux helps you manage “global” state - state that is needed across many parts of your application.
The patterns and tools provided by Redux make it easier to understand when, where, why, and how the state in your application is being updated, and how your application logic will behave when those changes occur.
Redux guides you towards writing code that is predictable and testable, which helps give you confidence that your application will work as expected.
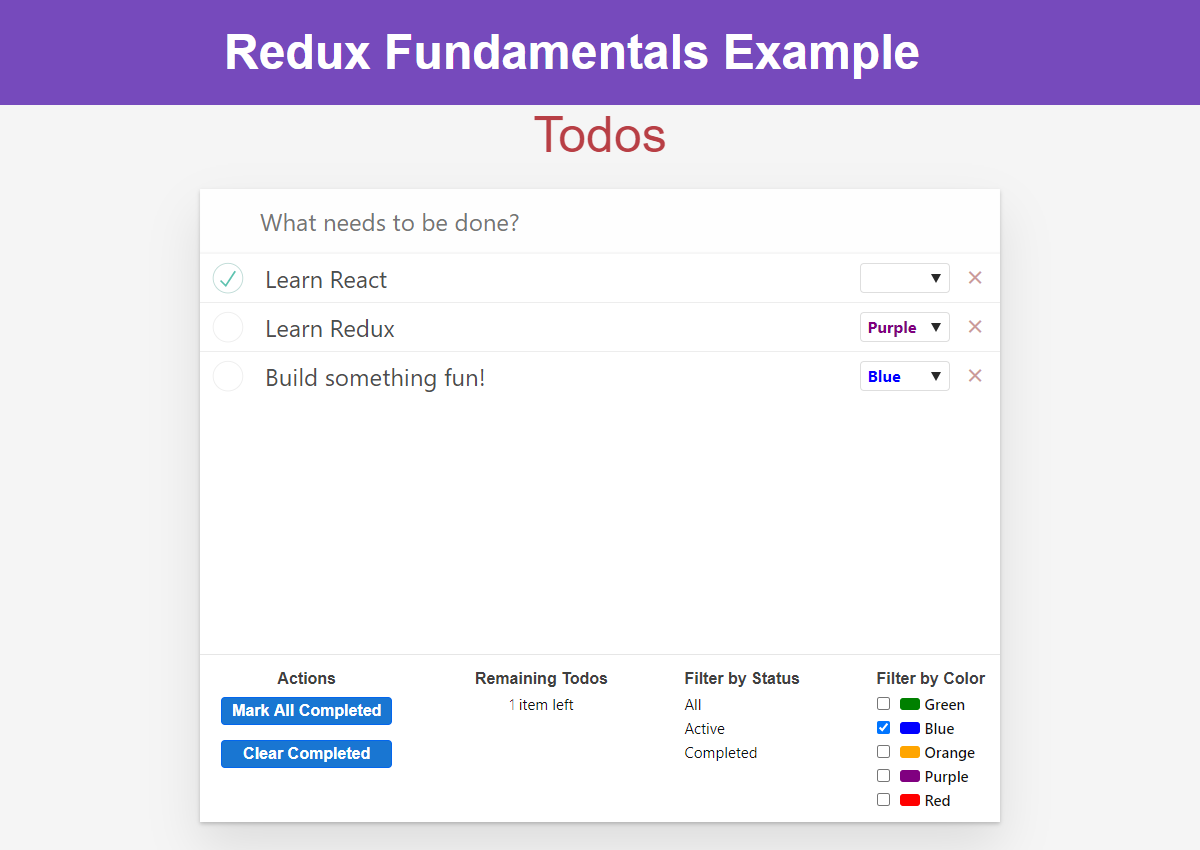
2.3 Example: todo
3 local storage
We could add local storage to our basic todo
The todos state is stored in the local storage using the localStorage.setItem method.
It is initialized with the stored todos from the local storage in the first useEffect hook. Whenever the todos state is updated, the second useEffect hook is triggered, and the updated todos are stored in the local storage using localStorage.setItem.
Todos.jsx
// ...
const Todos = () => {
const [todos, setTodos] = useState([]);
useEffect(() => {
const storedTodos = localStorage.getItem(LOCAL_STORAGE_KEY);
if (storedTodos) {
setTodos(JSON.parse(storedTodos));
}
}, []);
useEffect(() => {
localStorage.setItem(LOCAL_STORAGE_KEY, JSON.stringify(todos));
}, [todos]);
const fetchTodos = async () => {
// Fetching todos from API (unchanged code)
// ...
};
const addTodo = (newTodo) => {
// Adding todo to the state and localStorage
setTodos([...todos, newTodo]);
};
const updateTodo = async (id) => {
// Updating todo in the state and localStorage
const updatedTodos = todos.map((todo) => {
if (todo.id === id) {
return { ...todo, completed: !todo.completed };
}
return todo;
});
setTodos(updatedTodos);
};
const deleteTodo = async (id) => {
// Deleting todo from the state and localStorage
const filteredTodos = todos.filter((todo) => todo.id !== id);
setTodos(filteredTodos);
};
// ...
return (
<ApiContext.Provider
value={{ todos, addTodo, updateTodo, deleteTodo }}>
{/* ... */}
</ApiContext.Provider>
);
};
export default Todos;