classDiagram
class GeneralOperations {
<<interface>>
+createAccount(): void
+searchBooks(query: String): void
}
class UserOperations {
<<interface>>
+borrowBook(book: Book): void
+returnBook(book: Book): void
+checkBorrowedBooks(): void
}
class LibraryMember {
<<abstract>>
+id: String
+address: String
+phoneNumber: String
}
class Member {
<<abstract>>
+name: String
+surname: String
nationality: String
+birthdate: Date
}
class StaffOperations {
<<interface>>
+addBook(book: Book): void
+removeBook(book: Book): void
+updateBookDetails(book: Book): void
+registerUser(user: User): void
+removeUser(user: User): void
+updateUserDetails(user: User): void
+generateReports(): void
}
class User {
-libraryCardNumber: String
-borrowedBooks: ArrayList<Book>
+User()
}
class Author {
-deathdate: Date
-books: Book
+author()
}
class Staff {
-staffId: String
-position: String
-registeredUsers: ArrayList<User>
-libraryBooks: ArrayList<Book>
+Staff()
}
class Book {
-title: String
-author: Author
-publisher: String
-year: int
-isbn: String
-status: String
+Book()
+getStatus(): String
}
GeneralOperations <|.. LibraryMember
UserOperations <|.. User
LibraryMember <|.. User
LibraryMember <|.. Staff
Member <|.. Author
Member <|.. LibraryMember
StaffOperations <|.. Staff
Auth
Lab#SB00-1: Library UML
Spring Boot Library Management UML
📘 Spring Boot Lab#SB00-1: Library UML We are going to evolve the current Java SE Libraryproject into a Spring Boot Library Management System with a H2 DB and web with Thymeleaf.
The resulting
Spring Boot Projectwould be similar to the currentJava SE LibraryProject, with the addition of theSpring Bootannotations and theH2 databaseconfiguration.
The classes would be annotated with the
@Entityannotation to indicate that they are persistent entities, and the repositories would be annotated with the@Repositoryannotation.
The services would be annotated with the
@Serviceannotation, and the controllers would be annotated with the@Controllerannotation.
The
Thymeleaftemplates** would be created in the resources/templates folder** of the project.
1 From LibraryProject to LibraryManagement
1.1 Create a new Spring Boot project & H2 DB
Create a new Spring Boot project: The first step would be to create a new Spring Boot project in the preferred IDE or text editor.
The project can be created using Spring Initializr, which will create the necessary file structure and dependencies.
Configure the H2 database: In the newly created project, configure the H2 database by adding:- the H2 dependency in the
pom.xmlfile, - and also create a new
application.propertiesfile - set the database properties such as:
- the database URL,
- username,
- and password.
- the H2 dependency in the
1.2 Model & Entities
Create a Book Entity: To represent a book in the library management system, create a Book @Entity
It could include attributes such as title, author, publisher, year, ISBN, and status. The status attribute will indicate whether the book is available, borrowed or reserved.
Create a User Entity: To represent a user in the system, create a User entity that includes attributes such as library card number, name, surname, nationality, birthdate, and borrowed books.Create Author Entity: To represent an author in the system, create an Author entity that includes attributes such as deathdate, books, name, and surname.Create Staff Entity: To represent staff members in the system, create a Staff entity that includes attributes such as staff ID, position, registered users, and library books.
1.3 Domains: @Controller, @Service and @Repository
Create Repositories: To access the data stored in the database, create repositories for each entity. The repositories will provide the methods to create, read, update, and delete the data.Create Services: Create services that will implement the business logic of the system by calling the repository methods.
The services will provide the methods to search for books, borrow a book, return a book, add a book, remove a book, update book details, register a user, remove a user, update user details, and generate reports.
Create Controllers: Create controllers that will handle the HTTP requests from the web interface by calling the service methods.
The controllers will provide the methods to create a user account, search for books, borrow a book, return a book, add a book, remove a book, update book details, register a user, remove a user, update user details, and generate reports.
1.4 HTML Thymeleaf
1.4.1 Modern server-side Java template engine
1.4.2 Create Thymeleaf
Create Thymeleaf templates: To create the web interface of the system, create Thymeleaf templates for each of the controller methods. The templates will be used to display the data and also to handle the user input.
Thymeleaf is a modern server-side Java template engine for both web and standalone environments.
Thymeleaf’s main goal is to bring elegant natural templates to your development workflow — HTML that can be correctly displayed in browsers and also work as static prototypes, allowing for stronger collaboration in development teams.
1.5 Test
- Test the system: Test the system by running it and making sure that all the functionalities work as expected.
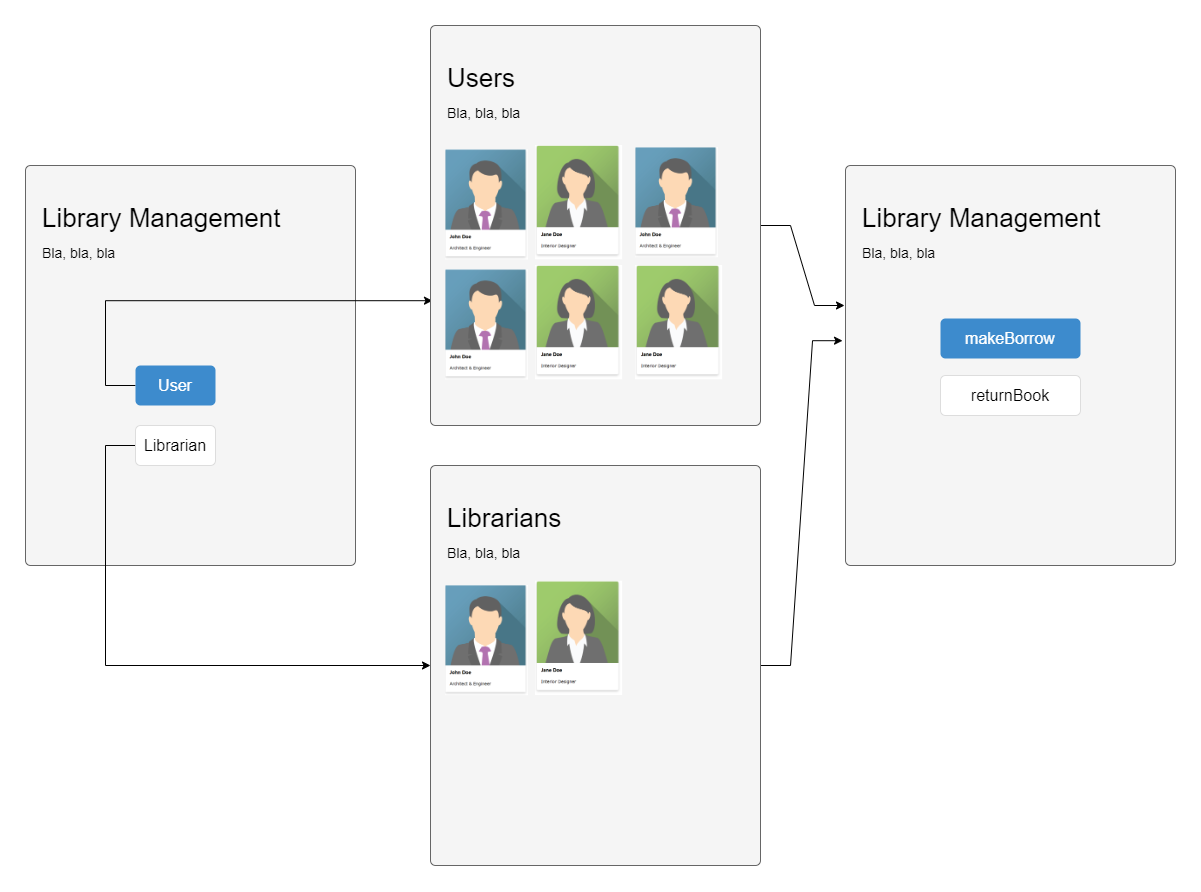
2 MockUp
2.1 Core use-case: borrowBook() and returnBook() with user and librarian
3 Discussion Solving: UML
Within Spring Boot Project
classDiagram
class WebController {
-bookService: BookService
-userService: UserService
+WebController()
+home(model: Model): String
+searchBooks(model: Model, query: String): String
+register(model: Model): String
+addUser(model: Model, user: User): String
+borrow(model: Model, bookCopyId: String): String
+returnBook(model: Model, bookCopyId: String): String
+checkBorrowedBooks(model: Model): String
}
class BookService {
-bookRepository: BookRepository
-bookCopyRepository: BookCopyRepository
-borrowRecordRepository: BorrowRecordRepository
+BookService()
+addBook(book: Book): void
+removeBook(isbn: String): void
+getBook(isbn: String): Book
+searchBooks(query: String): List<Book>
+getAvailableBookCopies(isbn: String): List<BookCopy>
+getBorrowedBookCopies(user: User): List<BookCopy>
+borrowBook(user: User, bookCopyId: String): void
+returnBook(user: User, bookCopyId: String): void
}
class UserService {
-userRepository: UserRepository
-borrowRecordRepository: BorrowRecordRepository
+UserService()
+registerUser(user: User): void
+removeUser(libraryCardNumber: String): void
+updateUserDetails(user: User): void
+getUser(libraryCardNumber: String): User
+getBorrowedBooks(user: User): List<BookCopy>
+getBorrowHistory(user: User): List<BorrowRecord>
}
WebController --> BookService
WebController --> UserService
BookService --> BookRepository
BookService --> BookCopyRepository
BookService --> BorrowRecordRepository
UserService --> UserRepository
UserService --> BorrowRecordRepository
Just the Controller and Service
classDiagram
class BookCopy {
-id: String
-status: String
-book: Book
+BookCopy(book: Book)
+getStatus(): String
}
class BorrowRecord {
-id: String
-user: User
-bookCopy: BookCopy
-borrowDate: LocalDateTime
-returnDate: LocalDateTime
+BorrowRecord()
+setReturnDate(returnDate: LocalDateTime): void
}
Book --> Author
Book --> BookCopy
BookCopy --> Book
BookCopy --> BorrowRecord
User --> BorrowRecord
User --> BookCopy
BorrowRecord --> User
BorrowRecord --> BookCopy