Lab#SE03-2: Library/Book, Sprint Zero
Java SE Lab 03 part 2
📘 Linux Lab#SE03-2: Library/Book Sprint Zero
Before define what a Sprint Zero really is, let’s see what it isn’t.
A Sprint Zero is not the phase in which:
- the team is put together: a team must already be in place.
- for setting up infrastructure which should already be implemented or easily implemented on demand.
- should not involve adding products to a backlog or consider planning as classical project management.
The main goal of a Sprint Zero is to deliver some usable value that can be built upon by the next team. Sprint Zeros are required to:
- Create the project’s
skeleton, including research spikes. Keep design minimal.- Develop a small number of
storiesto completion. - Be low velocity and lightweight.
More specifically, the deliverables of a Sprint Zero should be as follows:
- A
usablepiece of code, however small. - A
minimalenvironment for writing code. - A
prioritizationof features or a list of stories. - A
release planassigning each story to a Sprint. - A plan for the most likely implementation of
features.
1 Sprint Zero hats&jobs
1.1 Architecture and first draft
1.1.1 Tasks/Requirements list
Let’s take the example of the Library Lab#SE03-1 to define a graph with the requirements/tasks for the Sprint Zero deriverables:
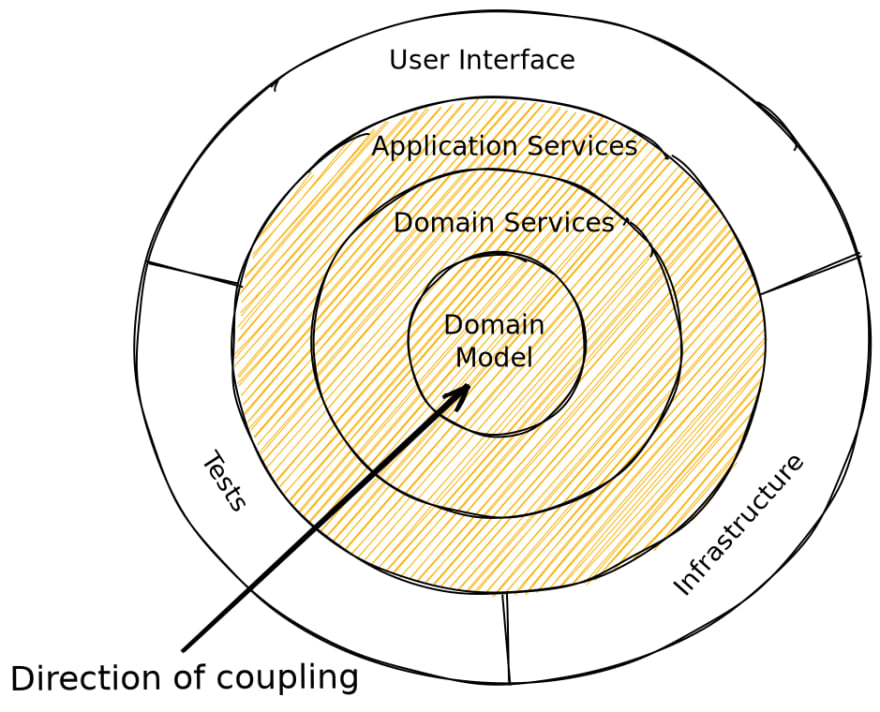
1.1.2 Onion Architecture
The layers are of Onion Architecture and sublayers are:
Infrastructure, where our database, file system, or any external web service we depend on live.Tests: unit, integration, end-to-end. How we validate our business cases.User Interface, how our users interact with the code we have built. - Application Services layer (sometimes known as the Transport/Access Layer).Domain Serviceslayer. In this layer is where the majority of our business logic lives, it carries out the operations to turn A into B, input into output, egg into chicken.- The core layer, the
Domain Modellayer which is the representation of the high level data objects we use.
1.2 Features: core use-case: user-borrows-a-book
1.2.1 Use-Story
As a user, I want to borrow a book with my
documentId, so that I may read and return it at due date that the system says.
1.2.2 Mock-up
1.3 Pieces of code
1.3.1 UUID
The full form of UUID is Universally Unique Identifier. A UUID represents a 128-bit value that is unique. The standard representation of UUID uses hex digits.
For example:
3c0969ac-c6e3-40f2-9fc8-2a59b8987918
cb7125cc-d78a-4442-b21b-96ce9227ef511.3.2 BorrowManager class
1.3.3 faker Users and Books
public static void createBooks(int number) {
// create faker object to use as
// builder for book
Faker faker = new Faker();
Book newbook;
for (int i = 0; i < number; i++) {
// create newbook without args
newbook = new Book();
// some people get nervous with this
// be careful ...
String bookId = InterfaceUtils.createUUID();
newbook.setISBN(bookId);
// title's book
String bookTitle = faker.book().title();
newbook.setTitle(bookTitle);
// year's book
int bookYear = faker.number().numberBetween(1000, 2023);
newbook.setYear(bookYear);
// borrows' book
List<Borrow> borrows = new ArrayList();
newbook.setBorrows(borrows);
// author's book
Author newauthor = new Author();
newbook.setAuthor(newauthor);
// add to hashmap
books.put( bookId, newbook);
// kill object
newbook = null;
}
}1.4 Tests
1.4.1 borrow object test
1.4.2 make-a-borrow test
Test to make-a-borrow operation by simulate-console
We decide to discuss this test in the near future, not now. It is more diffucult and complex than we thought.