Lab#RE01-1: API Rest Axios
ReactJS API Rest Axios & Render Component
📘 React JS Lab#RE01-1: API Rest and Axios
In this lab, we will be using:
- the
Open Library API, which is aRESTful API, to create a React app that will display a list of books. - We will use the
Axioslibrary to make HTTP requests to the API and retrieve the data in JSON format. - We will display the
book datain a table with four fields for each book: title, year, ISBN, pages, and author. - We will also add a
loading stateto show the user that the app is retrieving data from the API.
The lab will demonstrate how to use a RESTful API with React to build a functional web application.
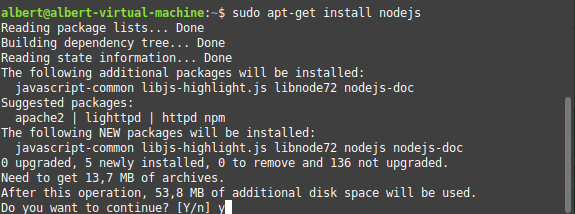
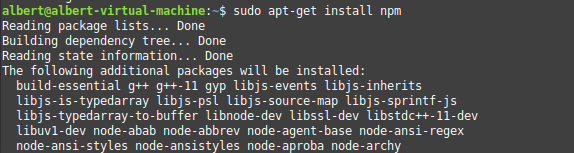
1 Install nodejs & npm
References:
1.1 from repo
1.2 update/last version
1.2.1 download
1.2.2 terminal
Often the installed Node.js version from the repositories will be outdated. If you need to upgrade Node.js to the latest version you can use module n.
The module n will take care for the upgrade of Node.js when it’s installed from PPA.
Install module n by:
The command "npm install n -g" is used to install the "n" package globally on a system.
The "n" package is a node version manager, which allows you to easily switch between different versions of Node.js on your system. With this package, you can install multiple versions of Node.js on your system and easily switch between them as needed.
The "-g" flag indicates that the package should be installed globally, which means that it will be available to all users on the system, and not just the current user.
Then you can install the stable Node.js by:
or the latest:
1.3 Node Version Manager
“n” and “nvm” are both popular Node.js version managers, but they differ in some key ways.
“n” is a simple, lightweight Node.js version manager that is designed to be easy to use and install. It has a small footprint and allows you to quickly switch between different versions of Node.js using a command-line interface. “n” is also designed to be compatible with other package managers like npm, so you can easily install and manage Node.js modules alongside different versions of Node.js.
In contrast, “nvm” (Node Version Manager) is a more complex and feature-rich version manager. It allows you to manage multiple versions of Node.js, as well as install different versions of npm and use them alongside each Node.js version. It also has more advanced features, such as the ability to specify default Node.js versions and aliases for specific versions.
nvm allows you to quickly install and use different versions of node via the command line.
2 API Rest
An API (Application Programming Interface) is a set of protocols, routines, and tools that allow different software applications to communicate with each other. An API acts as a messenger that takes a request from one application and returns a response back to the requesting application.
REST (Representational State Transfer) is a software architectural style for building web services. It is based on HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and is commonly used for creating APIs. A RESTful API allows different software applications to communicate with each other by using HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE to access and manipulate data.
An Open API is an API that is publicly available and can be used by developers to build software applications. An Open API typically includes documentation and developer tools to help developers understand how to use the API.
The Open Library API is a RESTful API that provides access to the data stored in the Open Library project. The Open Library project aims to create a web page for every book ever published. The API allows developers to retrieve information about books, authors, subjects, and more.
The two Open Library API endpoints we are going to use are:
- Open Library Books This endpoint provides documentation for the Open Library Books API. It includes information on how to use the API to search for books, retrieve book details, and access other book-related information.
- Open Library Books: get 100 books This endpoint is used to retrieve a list of up to 100 books from the Open Library API. The
q=*parameter is used to search for all books, and the limit=100 parameter limits the results to 100 books. The response data is in JSON format and includes information like the book title, author, publication date, and more.
3 Create app
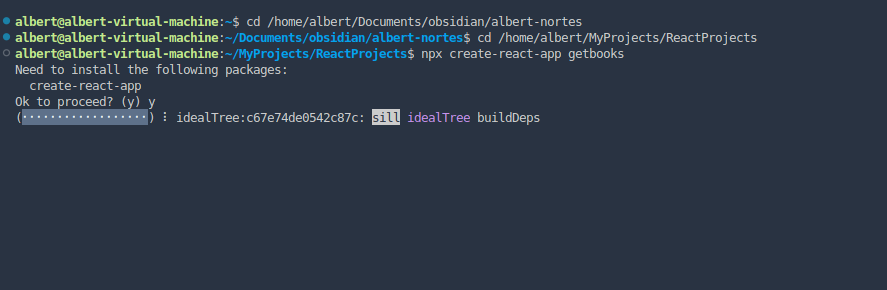
First, let’s create a new React app using Create React App by running the following command in your terminal:
to create a React App named books, or
to create a React App named hola.
Once the app is created, navigate into the project folder and install Axios, a popular library for making HTTP requests:
Now, let’s create a new component called BookList that will fetch and display the list of books:
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import axios from 'axios';
const BookList = () => {
const [books, setBooks] = useState([]);
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(true);
useEffect(() => {
const fetchBooks = async () => {
const response = await axios.get(
'https://openlibrary.org/search.json?q=*&limit=100'
);
const booksData = response.data.docs;
setBooks(booksData);
setIsLoading(false);
};
fetchBooks();
}, []);
return (
<>
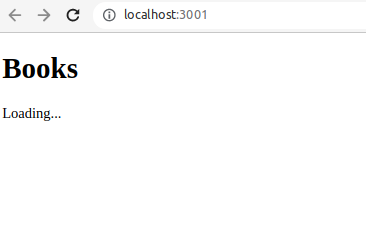
<h1>Books</h1>
{isLoading ? (
<p>Loading...</p>
) : (
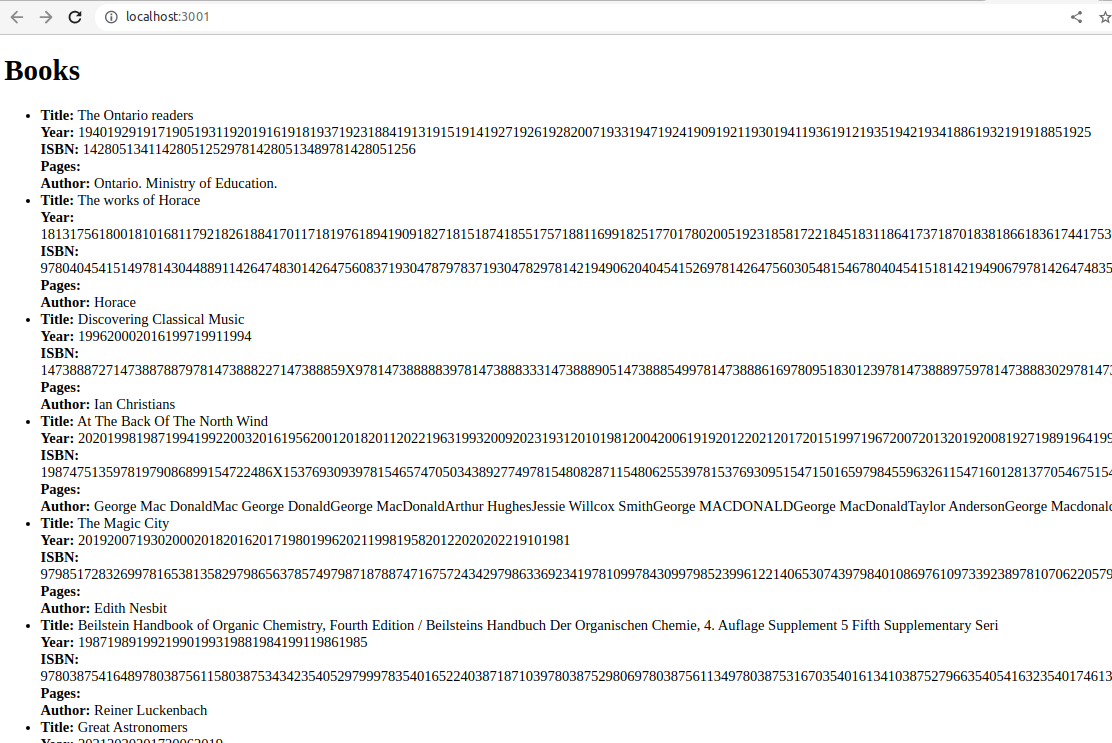
<ul>
{books.map((book) => (
<li key={book.key}>
<strong>Title:</strong> {book.title} <br />
<strong>Year:</strong> {book.publish_year} <br />
<strong>ISBN:</strong> {book.isbn[0]} <br />
<strong>Pages:</strong> {book.number_of_pages} <br />
<strong>Author:</strong> {book.author_name}
</li>
))}
</ul>
)}
</>
);
};
export default BookList;Now, let’s add the BookList component to our App component:
Finally, let’s start the development server and see the list of books in our browser:
Open yo browser on http://localhost:3000/ or http://localhost:3001/ if 3000 is occupied.
4 handle error
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import axios from 'axios';
const BookList = () => {
const [books, setBooks] = useState([]);
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(true);
const [isError, setIsError] = useState(false);
useEffect(() => {
const fetchBooks = async () => {
try {
const response = await axios.get(
'https://openlibrary.org/search.json?q=*&limit=100'
);
const booksData = response.data.docs;
setBooks(booksData);
setIsLoading(false);
} catch (error) {
setIsError(true);
setIsLoading(false);
}
};
fetchBooks();
}, []);
return (
<>
<h1>Books</h1>
{isLoading && !isError && <p>Loading...</p>}
{!isLoading && isError && <p>Error: Could not fetch books</p>}
{!isLoading && !isError && (
<ul>
{books.map((book) => (
<li key={book.key}>
<strong>Title:</strong> {book.title} <br />
<strong>Year:</strong> {book.publish_year} <br />
<strong>ISBN:</strong> {book.isbn[0]} <br />
<strong>Pages:</strong> {book.number_of_pages} <br />
<strong>Author:</strong> {book.author_name}
</li>
))}
</ul>
)}
</>
);
};
export default BookList;